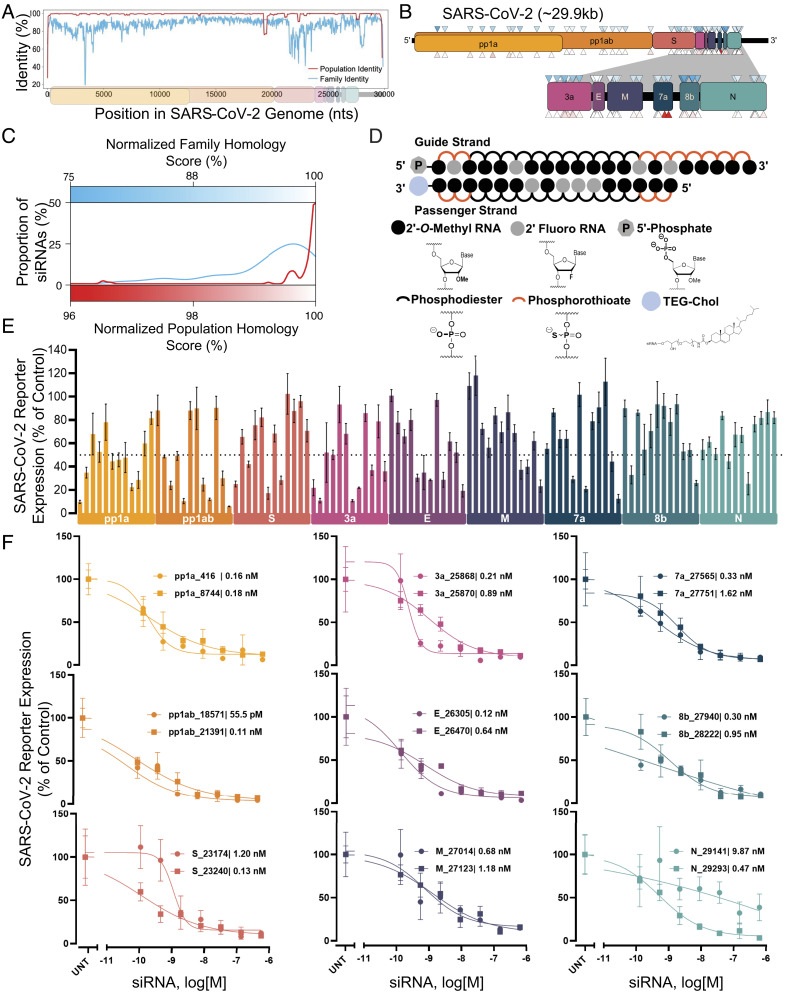
Fig. 1.
Design and screening of fully chemically modified siRNAs targeting conserved SARS-CoV-2 gene regions. (A) Population identity indicates that from the alignment of the SARS-CoV-2 target genome with SARS-CoV-2 genomes from the COVID-19 patient. Family identity indicates that from the alignment of the SARS-CoV-2 target genome with the most closely related SARS-CoVs. All identities are averaged over a sliding window of fifty bases to facilitate visualization. (B) siRNAs were designed to target the open reading frame of the SARSCoV-2 genome indicated by triangles. Triangle colors correspond to the homology scores in (C)-upper triangles for family homology score and lower triangles for population homology score. (C) Each siRNA sequence was scored based on its homology to the SARS-CoV-2 population (red) and family (blue). (D) Schematic of the fully chemically modified siRNA. (E and F) Percent expression of SARS-CoV-2 reporter in HeLa cells 72 h after uptake of siRNA (n = 3; E: 1.5 µM, F: concentration indicated). Reporter expressions were assayed using the psiCHECK-2 reporter system for SARS-CoV-2. Data presented relative to UNT (mean ± SD of independent biological replicates). Target regions of SARS-CoV-2 are indicated in each graph. The dotted line indicates 50% silencing (E). IC50 values of each siRNA are indicated on each graph (F). UNT, untreated control.