Figure 9.
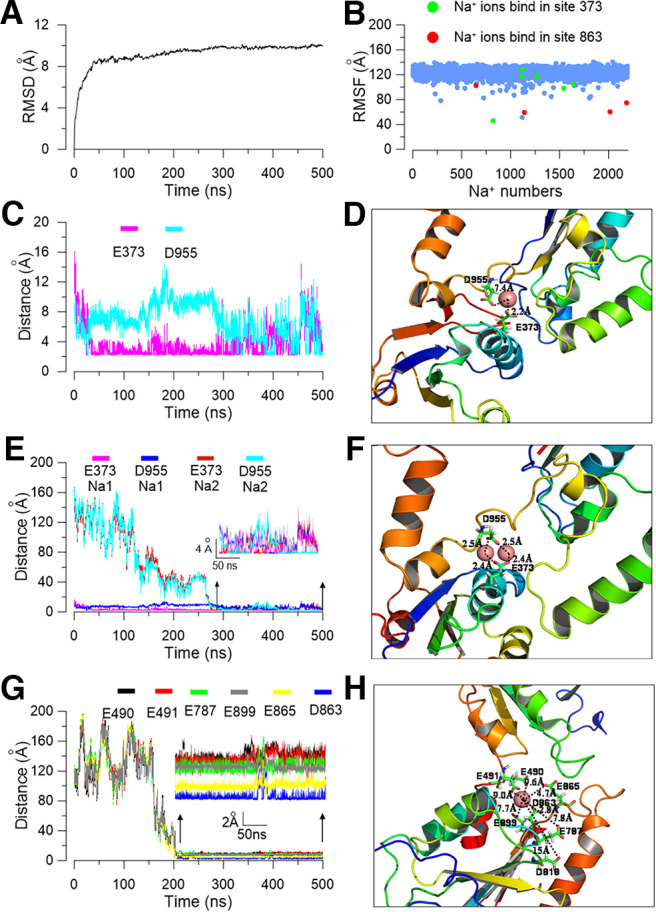
Molecular simulation shows two potential sodium binding sites in the C terminus of the Slack channel. A, The rmsD of the backbone of the Slack channel during MD simulation. B, The rmsF of total Na+ ions in the simulation system of a Slack channel homology model; the red-labeled sodium ions are in the E373 residue, while the green-labeled sodium ions are in the D863 position. C, The distances from the residing sodium ions to residues E373 and D955 in subunit b during the MD simulation process. D, A snapshot of the E373 sodium interaction site with only one sodium ion located between the E373 and D955 residues. E, During the MD simulation, the distances from two simultaneously resident sodium ions to residues E373 and D955 in the subunit c of the Slack channel. F, A snapshot of the simulated local structure of equilibrated coordinated sites with a conformation that two sodium ions simultaneously bind close to the E373 and D955 residues. G, The sodium ion distances to residues D863, E865, E787, E899, E490, and E491 in the acidic sodium pocket during the MD simulation in the Slack channel model. H, Simulated local structure of the acidic pocket formed by E490, E491, E787, D818, D863, and E865 amino acids of the Slack channel.
