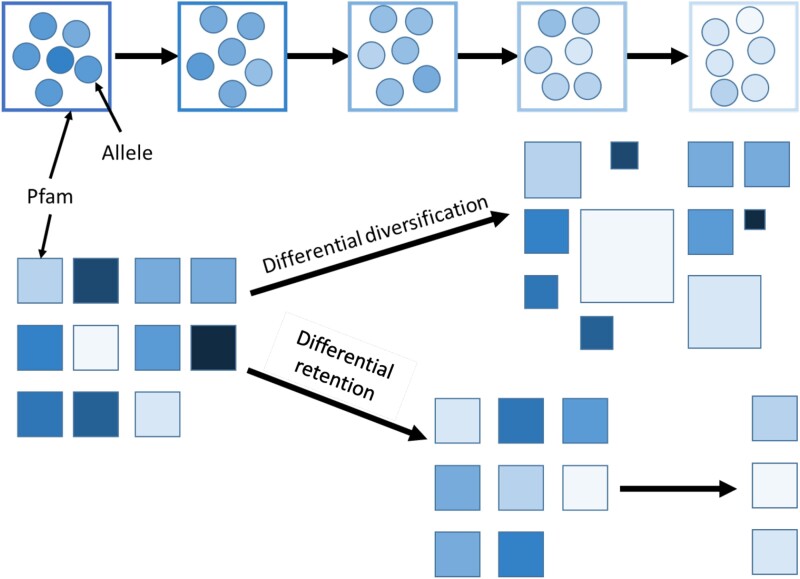
Fig. 1.
Alternative mechanisms/levels of directional selection over evolutionary time. Directional evolution in a trait with cohort age, represented by a change from dark to pale, can occur either via (top) descent with modification during which selected (pale) alleles replace other alleles, or (bottom) differential retention in which an initial diversity of Pfams is differentially retained. Differential diversification (middle) combines tendencies for duplication and tendencies for loss. Note that this is a level of selection situation; a Pfam is a clade of protein-coding sequences and their component alleles, and the same figure could be interpreted with individual interests in lieu of allele interests and clade interests in lieu of Pfam interests.