A 60-year-old man was referred for evaluation of a rectal submucosal tumor located 5 cm proximal to the anus ( Video 1, Fig. 1 ). Endoscopic ultrasonography revealed a 3-cm hypoechoic lesion originating from the muscular layer. The patient underwent submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection (STER) under sedation with propofol for diagnosis and treatment ( Fig. 2 ). A small horizontal incision was made at the anus and a submucosal pocket was created with injection of a mixture of hydroxyethyl starch and indigo carmine into the submucosal layer (GIF 190TH1; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan; and Flush Knife BTs 1.5 mm, FujiFilm, Tokyo, Japan). The tip of the tumor was enucleated ( Fig. 3 ), and then the intramuscular portion of the tumor was dissected with a square-tip knife (Square Knife; Endoaccess, Garbsen, Germany) using spray coagulation (VIO 3; Erbe, Tübingen, Germany). Dissection was advanced up to the level of the perirectal fat, while paying attention to avoid damage to the tumor capsule. The tumor was removed en bloc ( Fig. 4 ) and the mucosal entrance was closed with two clips. The procedure lasted for 1 hour. The patient was hospitalized for 1 night, received oral amoxicillin/clavulanic acid for 5 days, and had an uneventful recovery. Histology showed a benign gastrointestinal stromal tumor ( Fig. 4 ). STER is mainly applied in the stomach and esophagus 1 . This case report demonstrates the feasibility of this technique in the rectum.
Fig. 1.
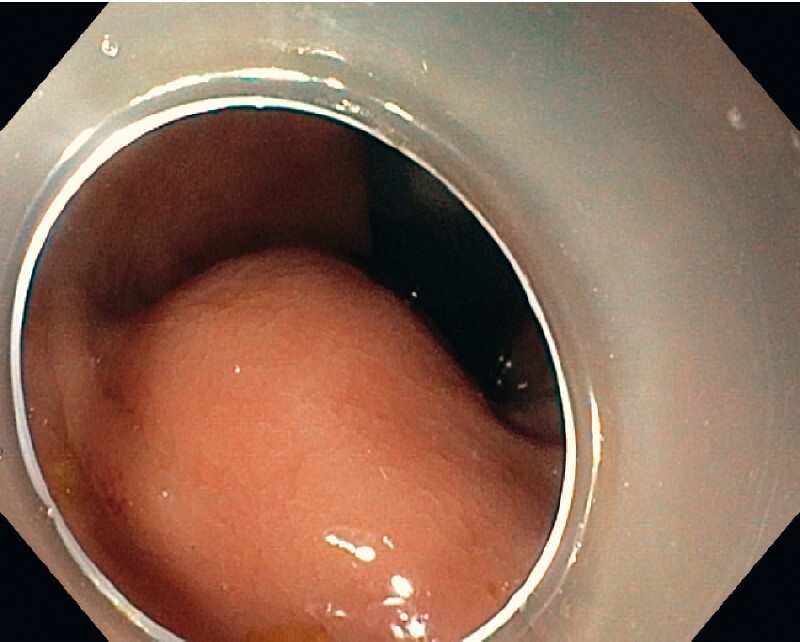
Submucosal tumor (3 cm) of the lower rectum.
Fig. 2.
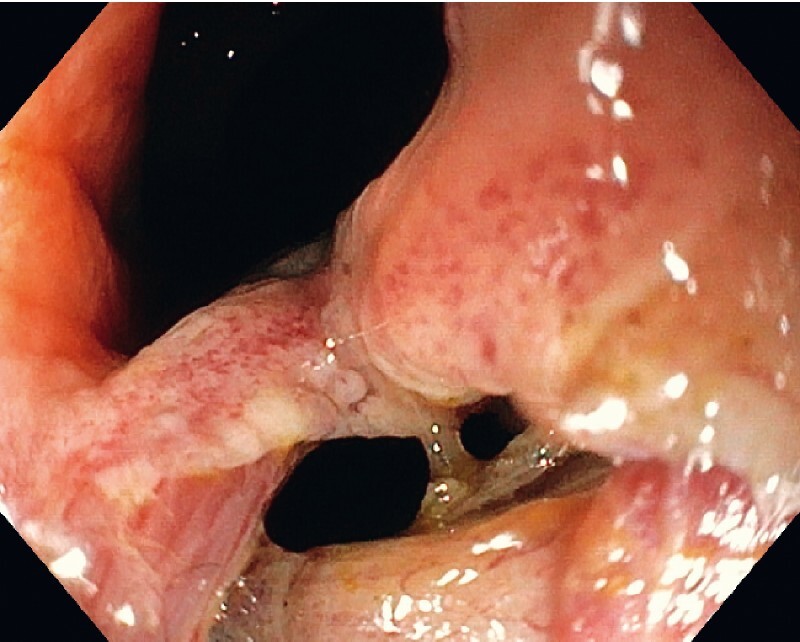
Mucosal entrance of the tunnel.
Fig. 3.
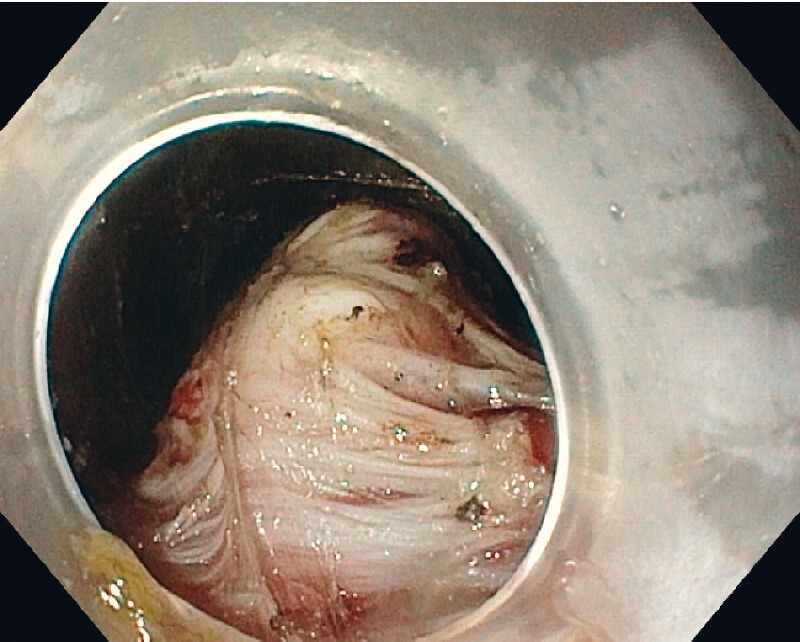
Partly enucleated tumor.
Fig. 4.
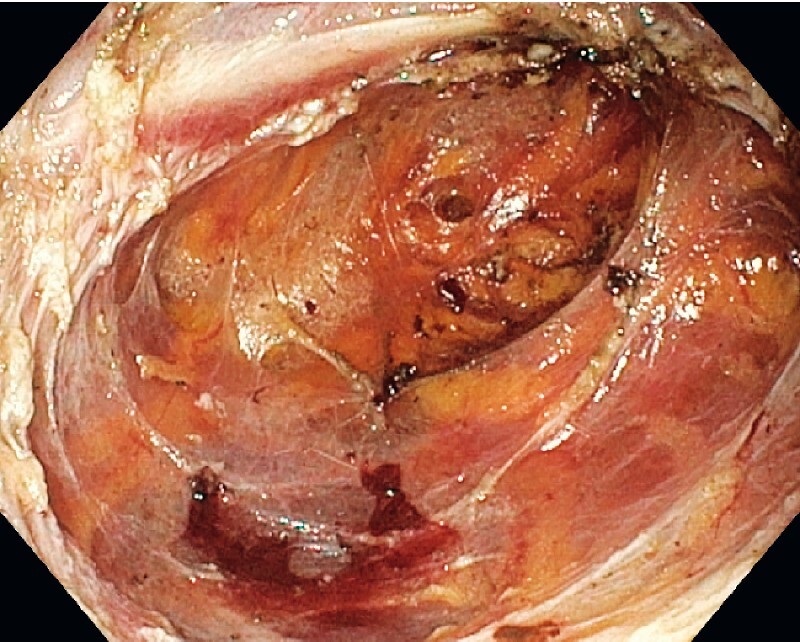
Inspection of the pocket at the end of the procedure. The perirectal fat is visible.
Video 1 Removal of a rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumor by means of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection.
Endoscopy_UCTN_Code_TTT_1AQ_2AD
Footnotes
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Endoscopy E-Videos : https://eref.thieme.de/e-videos .
E-Videos is an online section of the journal Endoscopy , reporting on interesting cases and new techniques in gastroenterological endoscopy. All papers include a high-quality video and are published with a Creative Commons CC-BY license. Endoscopy E-Videos qualify for HINARI discounts and waivers and eligibility is automatically checked during the submission process. We grant 100% waivers to articles whose corresponding authors are based in Group A countries and 50% waivers to those who are based in Group B countries as classified by Research4Life (see: https://www.research4life.org/access/eligibility/ ). This section has its own submission website at https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/e-videos
Reference
- 1.ASGE Technology Committee . Aslanian H R, Sethi A et al. ASGE guideline for endoscopic full-thickness resection and submucosal tunnel endoscopic resection. VideoGIE. 2019;4:343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2019.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


