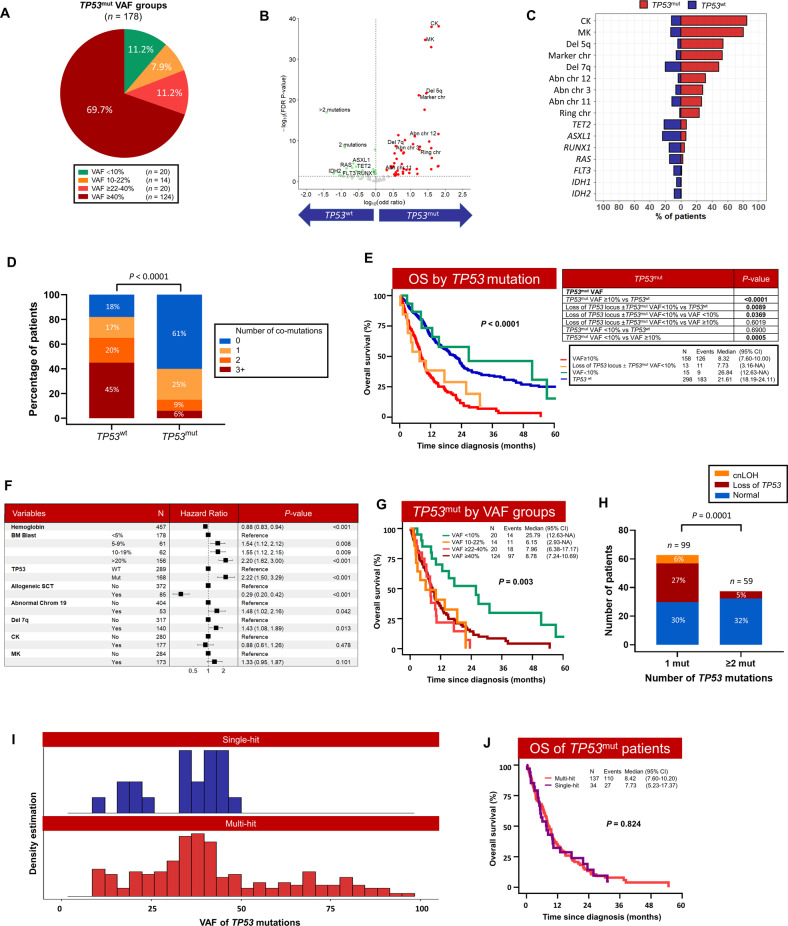
Fig. 2. TP53mut drive genomic instability and was associated with poor overall survival in therapy-related myeloid neoplasms (t-MN).
A Distribution of cases according to TP53mut VAF; B Volcano plot comparing cytogenetic aberration and somatic mutations in TP53mut and TP53wt t-MN. Chromosomal aberrancies highly prevalent in TP53mut (red) and somatic mutations enriched in TP53wt cohort (green). Genomic changes that are not differentially expressed between the two groups are shown in gray color; C Frequency of cytogenetic aberrations or driver oncogenic gene mutations in TP53wt and TP53mut t-MN; D Number of co-mutations in TP53wt and TP53mut t-MN; E Overall survival (OS) of TP53mut with VAF ≥10% or loss of TP53 locus was significantly poor compared to wild-type TP53 (TP53wt) and TP53mut with VAF < 10% t-MN; F Multivariate Cox-regression analysis of factors predicting overall survival in t-MN; G OS of TP53mut t-MN according to VAF cut-offs; H Frequency of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and copy neutral LOH (cnLOH) according to number of TP53mut; I Density estimation of VAF of single-hit and multi-hit TP53mut; J OS is equally poor in single- and multi-hit in t-MN.