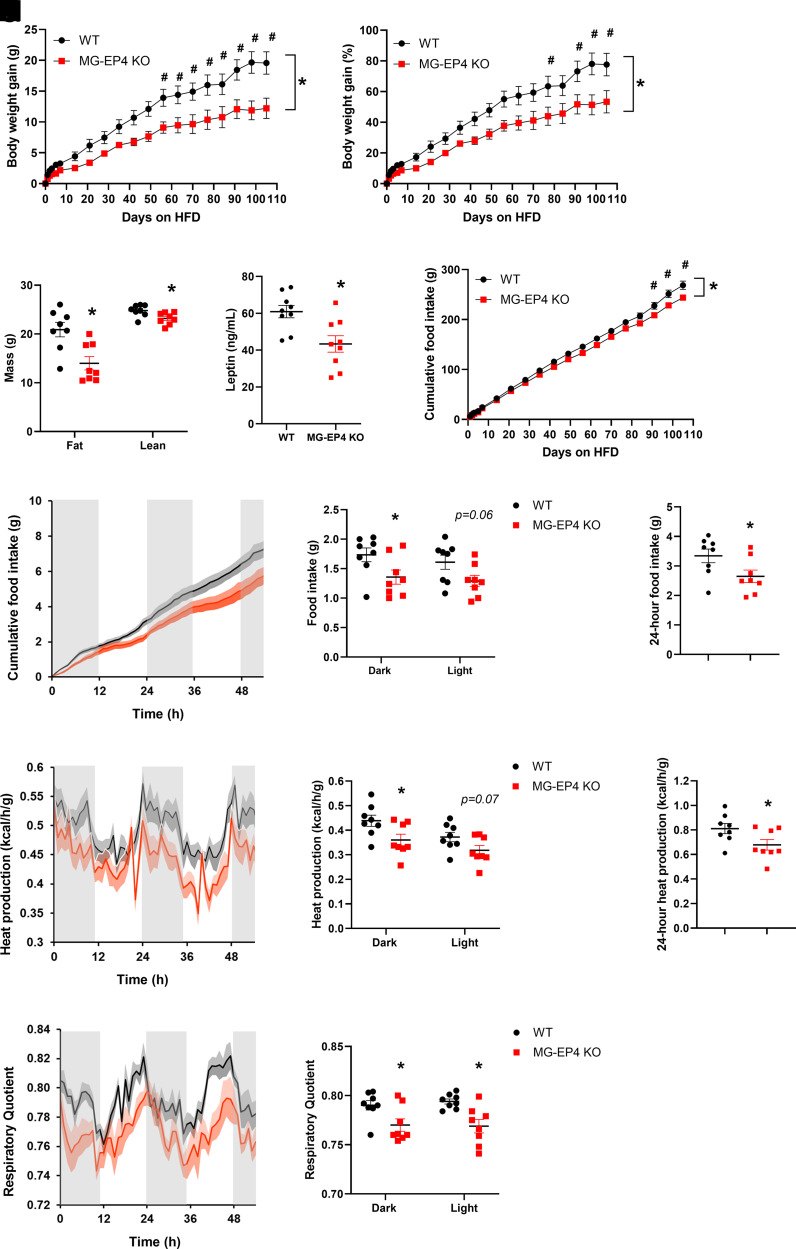
Figure 1.
Microglial EP4 deletion reduced susceptibility to DIO. A–E: Absolute body weight gain (A), percentage body weight gain (B), fat mass and lean mass (C), plasma leptin (D), and cumulative food intake (E) in male WT and MG-EP4 KO mice fed an HFD for 16 weeks (n = 8–9). F–H: Continuous measurements of cumulative food intake (F), binned dark cycle and light cycle food intake (G), and total 24-h food intake (H). I–K: Heat production traces (I), quantification of dark cycle and light cycle (J), and total heat production (K). L and M: Respiratory quotient traces (L) and quantification of dark cycle and light cycle respiratory quotient (M) following 16 weeks of HFD (n = 8). Body weight gain and cumulative food intake data analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Šidák test. Data in I–K analyzed by ANCOVA with body mass as covariate. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 for genotype × time interaction in ANOVA; #P < 0.05 for post hoc analysis.