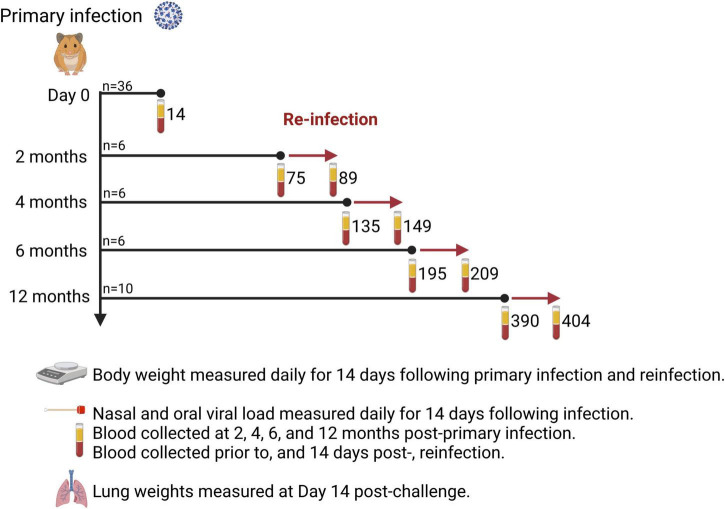
FIGURE 1.
Study design. Thirty-six (36) Syrian hamsters were infected intranasally with 1 × 105 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 (ancestral Wuhan strain). Hamsters were randomly assigned to one of five cohorts to determine the time interval (2, 4, 6, or 12 months) for reinfection. Bodyweight was measured daily for 14 days after primary infection and reinfection. Hamsters were sacrificed 14 days after reinfection and lung weights recorded. Blood samples were taken prior to reinfection and 14 days after reinfection to measure spike S1- and RBD-specific IgG titers and virus neutralizing antibody titers to ancestral Wuhan strain, Delta, and Omicron. The number of days post-primary infection are indicated for each blood sampling time-point. Created with BioRender.com.