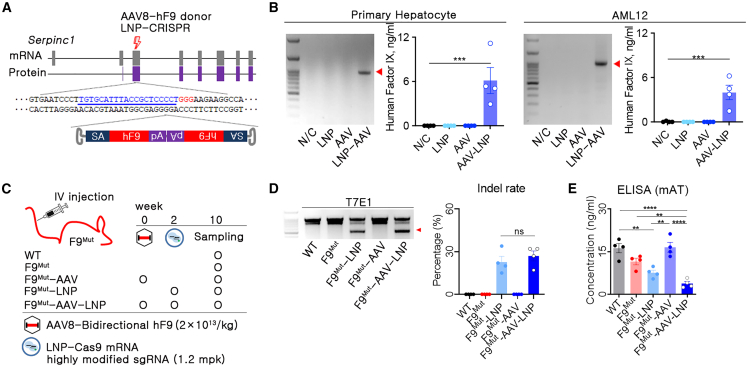
Figure 2.
In vivo human F9 gene KI into the Serpinc1 locus decreased antithrombin concentration in the blood
(A) Brief schematic representation of in vivo human (h)F9 KI into the third exon of Serpinc1 (thunder symbol: DSB site, blue letters: sgRNA binding sequences, red letters: protospacer adjacent motif [PAM] sequences; SA, splicing acceptor; hF9, coding sequence of hF9; pA, polyadenylation; LNP-CRISPR; lipid nanoparticle-packed SpCas9 mRNA and sgRNA). (B) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for KI and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for human factor IX (hFIX) was conducted after hF9 KI into the Serpinc1 locus using a primary hepatocyte and AML12 cell line (n = 4). (C) Brief information on experimental groups and injection schedule of genetic materials. (D) Identification of indel by T7E1 and calculation of indel rate using Sanger sequencing and algorithm-based analysis. (E) Mouse antithrombin (AT) concentration in the blood of different treatment groups, measured using ELISA. Each dot represents data from an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean, calculated using unpaired one-way ANOVA (∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.000).