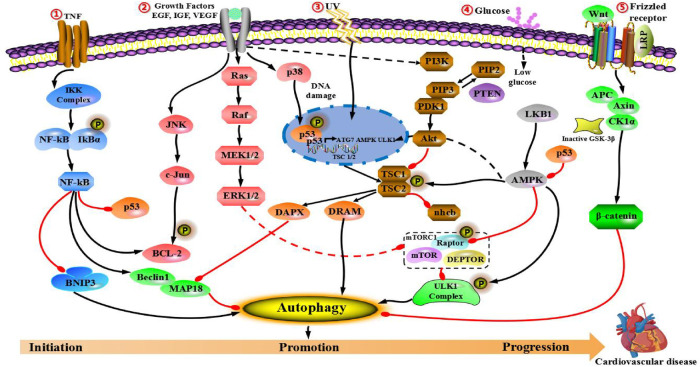
Figure 4.
Regulation of cross- interference between autophagy and main signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease. (1) NF-κB pathway of IKKα/β and NF-κB induces autophagy by increasing the expression levels of autophagy-related proteins, such as Beclin-1. (2) Growth factors (including EGF, IGF and VEGF) promote autophagy by modulating the autophagic process of JNK/c-Jun, Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/Akt. (3) p53 pathway: Autophagy is also mediated by the nuclear p53 activity, which is a transcribed factor under stressful conditions (such as ultraviolet rays, etc.). p53 induces the classic autophagic pathway mainly through PI3K/Akt/mTOR, AMPK/mTOR and ULK1 complex. (4) PI3K/Akt/mTOR and AMPK/mTOR receptor tyrosine kinases promote the transformation of PIP2 into PIP3 and the activation of PI3K. PTEN-induced dephosphorylation of PIP3 activates the AKT signal negatively regulated by PI3K. Amino acids and nutrient-rich conditions can initiate the activity of mTORC1 signal. By contrast, starvation and oxidative stress can inhibit the activity of mTORC1 signal and induce autophagy. (5) Wnt-β-catenin pathway: This pathway causes the activation and nuclear recruitment of β-catenin protein, so as to directly regulating autophagy.