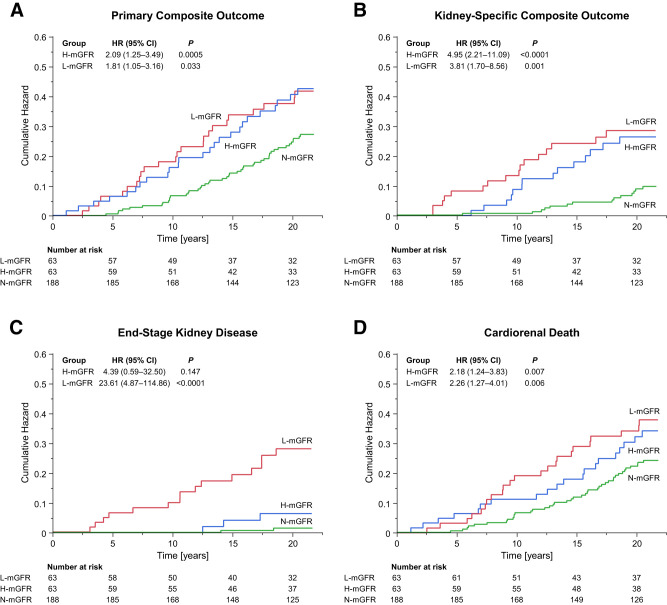
Figure 2.
A–D: Cumulative hazard of the primary composite outcome, kidney-specific composite outcome, ESKD, or cardiorenal death in participants with H-mGFR or L-mGFR compared with those with N-mGFR. The primary outcome was a composite of a doubling of serum creatinine levels from baseline, incident ESKD (defined as the initiation of dialysis, kidney transplantation, or an eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2), or death from cardiovascular or renal causes. The kidney-specific outcome was a composite of a doubling of serum creatinine level, ESKD, or death from renal cause. Cox proportional hazards regression models adjusted for age, sex, BMI, diabetes type and duration, HbA1c, systolic blood pressure, and log-transformed albuminuria were used to calculate HRs 95% CIs for the H-mGFR and L-mGFR groups vs. the N-mGFR group.