Figure 2. EGF activates Arf1 (mG*) and triggers the recruitment of GIV‐GEM on Golgi.
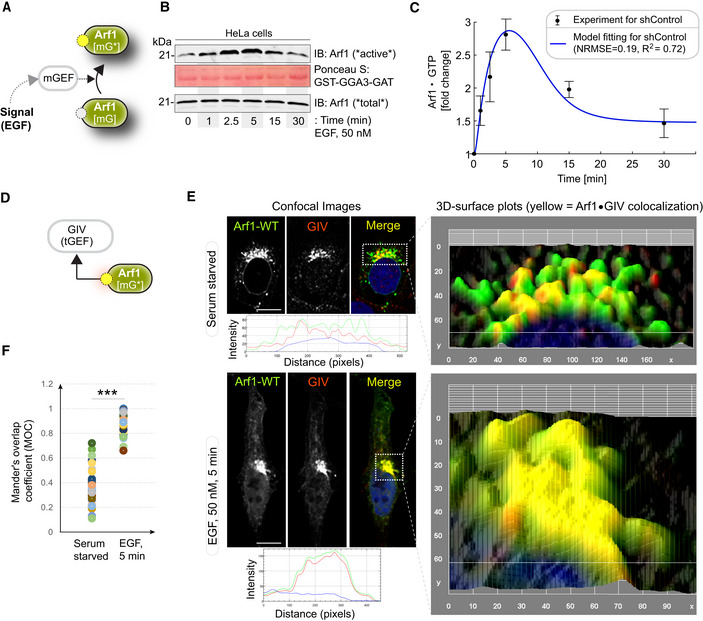
- Schematic showing the specific step being interrogated in panels (B, C), that is, Arf1 activation under EGF stimulation.
- Immunoblot shows GST‐GGA‐GAT domain bound Arf1 (active; top) and total Arf1 (input lysates; bottom) from equal aliquots of lysates of HeLa cells that were stimulated with EGF for the indicated time points prior to lysis.
- Graphs display the model fitting for Arf1 activation dynamics. The experimentally determined Arf1 activation (in B) dynamics are displayed as black dots with error bars, representing mean ± SEM (n = 3 biological replicates), and numerical simulation is shown by the blue continuous line.
- Schematic showing the specific step being interrogated in panels (E, F), that is, recruitment of GIV‐GEM on Golgi.
- HeLa cells expressing Arf1‐HA were serum starved overnight (E, top) and subsequently stimulated with EGF for 5 min (E, bottom) prior to fixation with PFA. Fixed cells were stained for Arf1 (HA; green) and GIV (red) and nuclei (DAPI; blue). Panels on the left show overlay of all three stains and representative RGB plots of sections through the Arf1‐stained pixels. Panels on the right display the magnified 3D surface plots of the boxed regions in the left panels. Scale bar = 10 μm.
- Scatter plot shows the Mandler's overlap coefficient (MOC) for Arf1‐HA and GIV colocalization in (E) that was calculated on 13–15 cells/experiment, n = 3 independent experiments. P‐values were determined using Mann–Whitney t‐test: ***P = 0.0002.
Source data are available online for this figure.
