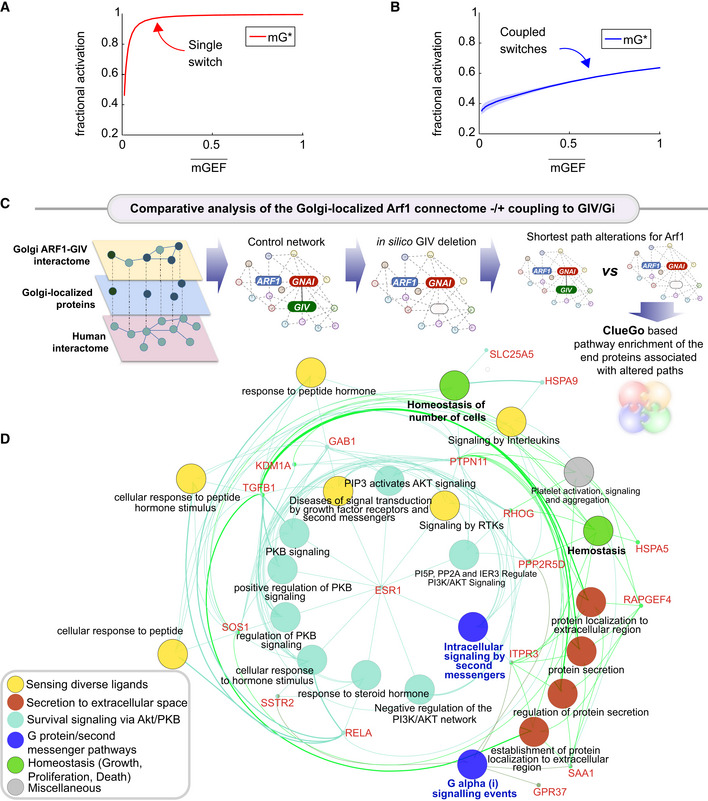
A comparative analysis of the Golgi‐localized Arf1 (mG) connectome with/without coupling to GIV (tGEF) and Gi (tGTPase). Workflow (C) shows how the list of Golgi‐localized Arf1 and GIV interacting proteins (Appendix Fig
S1
and Dataset
EV1) were used as “seeds” to construct a PPI network from the STRING database to fetch the linking nodes to connect the seed proteins. The network was then perturbed by
in silico deletion of GIV, followed by a topological analysis of how such perturbation impacts the shortest paths associated with Arf1 to all other nodes in the network (see
Materials and Methods). A network representation (D) using the ClueGo algorithm of the cellular processes associated with the end proteins that were most frequently encountered in the most impacted shortest paths associated with Arf1 (listed in Appendix Fig
S2
E). The deleted or newly added shortest paths were only considered using the differential network approach (see
Materials and Methods). The key in the lower left corner displays the color code of various overarching themes encountered in the network.