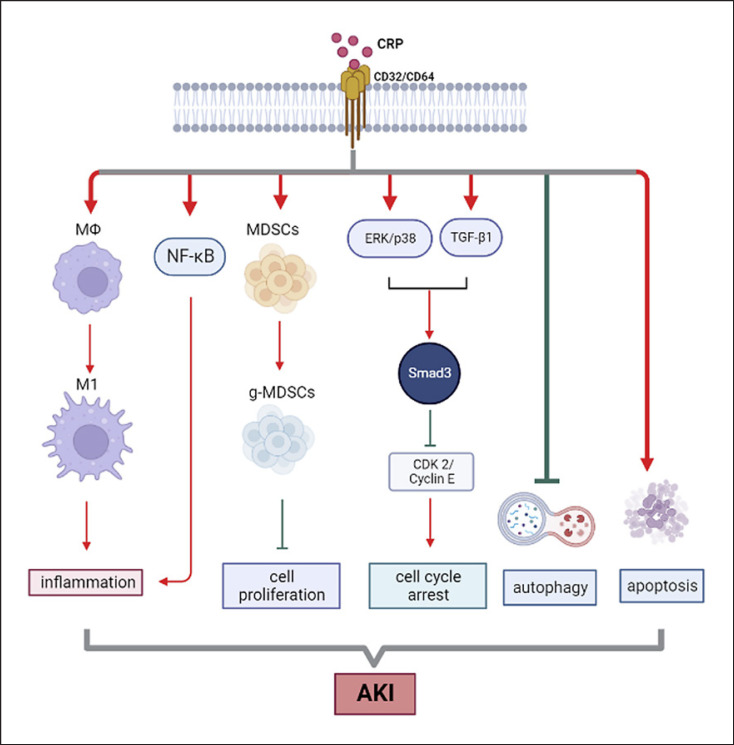
Fig. 1.
Mechanism of CRP in acute kidney injury (AKI). After binding with CD32/CD64, CRP promotes the activation of inflammation and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and apoptosis as well as inhibits autophagy and arrests the cell cycle by activating Smad3 via ERK/p38 and TGF-β1 signaling pathways, leading to the progression of AKI. Red arrows represent positive regulation of pathways or biological process, while the green lines represent negative regulation.