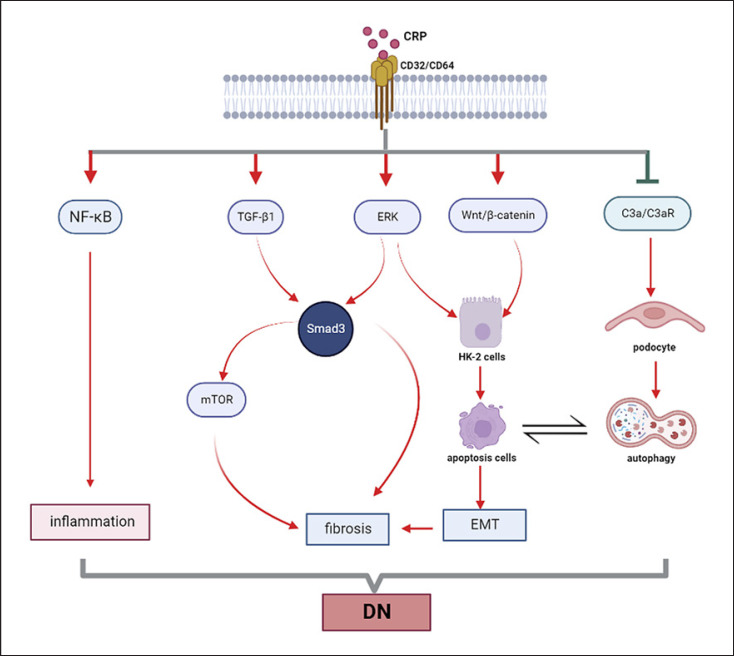
Fig. 3.
Mechanism of CRP in diabetic nephropathy. Under high-glucose condition, CRP induces renal fibrosis by Smad3-mediated mechanism. Meanwhile, the crosstalk between autophagy inhibited by CRP via C3a/C3aR pathway in podocyte, and apoptosis positively regulated by CRP via Wnt/β-catenin and ERK pathways in tubular epithelial cells, is related to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) which contribute to renal fibrosis. Similar to the mechanism of CRP in CKD, CRP could promote the activation of NF-κB pathway directly to induce inflammation in diabetic nephropathy (DN).