FIGURE 5.
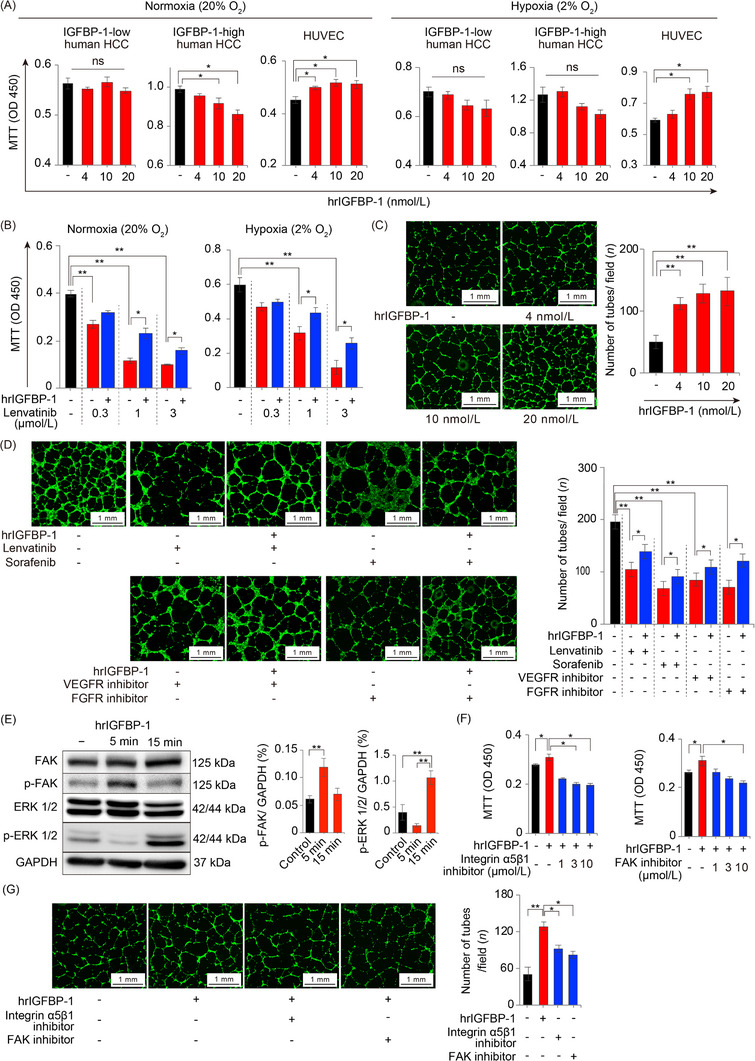
Functions of IGFBP‐1 on tumor cells and endothelial cells. (A) The effect of hrIGFBP‐1 on the proliferation of IGFBP‐1‐low human HCC (HuH7), IGFBP‐1‐high human HCC (HepG2) cells and HUVECs under normoxia and hypoxia for 48 h (n = 6 per group; *P < 0.05 vs. control, one‐way ANOVA). (B) The effect of hrIGFBP‐1 (10 nmol/L) on the proliferation of HUVECs in normoxia (20% O2; left) or hypoxia (2% O2; right) under lenvatinib exposure for 48 h (n = 6 per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA). (C) Quantification of the tube formation numbers stimulated with hrIGFBP‐1 (n = 3 per group) (**P < 0.001 vs. control, one‐way ANOVA). (D) The HUVEC angiogenesis (left) and proliferation (right) under exposure to antiangiogenic TKIs and 10 nmol/L hrIGFBP‐1 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA). (E) p‐FAK level is upregulated with 5 min hrIGFBP‐1 (10 nmol/L) stimulation and p‐ERK level is upregulated by 15 min hrIGFBP‐1 (10 nmol/L) stimulation. (F) The accelerated proliferation of HUVECs by hrIGFBP‐1 (10 nmol/L) stimulation is reduced by the integrin α5β1 inhibitor or FAK inhibitor (n = 6 per group). (G) Representative micrographs of the cavities (left) and quantification of the number of tubes in the cavities (right). Angiogenesis promoted by 10 nmol/L hrIGFBP‐1 is significantly reduced by the integrin α5β1 inhibitor (3 μmol/L) or FAK inhibitor (10 μmol/L) (n = 3 per group; *P < 0.05, one‐way ANOVA). Data are presented as means ± SEM.
Abbreviations: IGFBP‐1, insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein‐1; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; hrIGFBP‐1, human recombinant IGFBP‐1; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; p‐FAK, phospho‐FAK; p‐ERK, phospho‐ERK; VT, vehicle treatment; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; ns, no significance.
