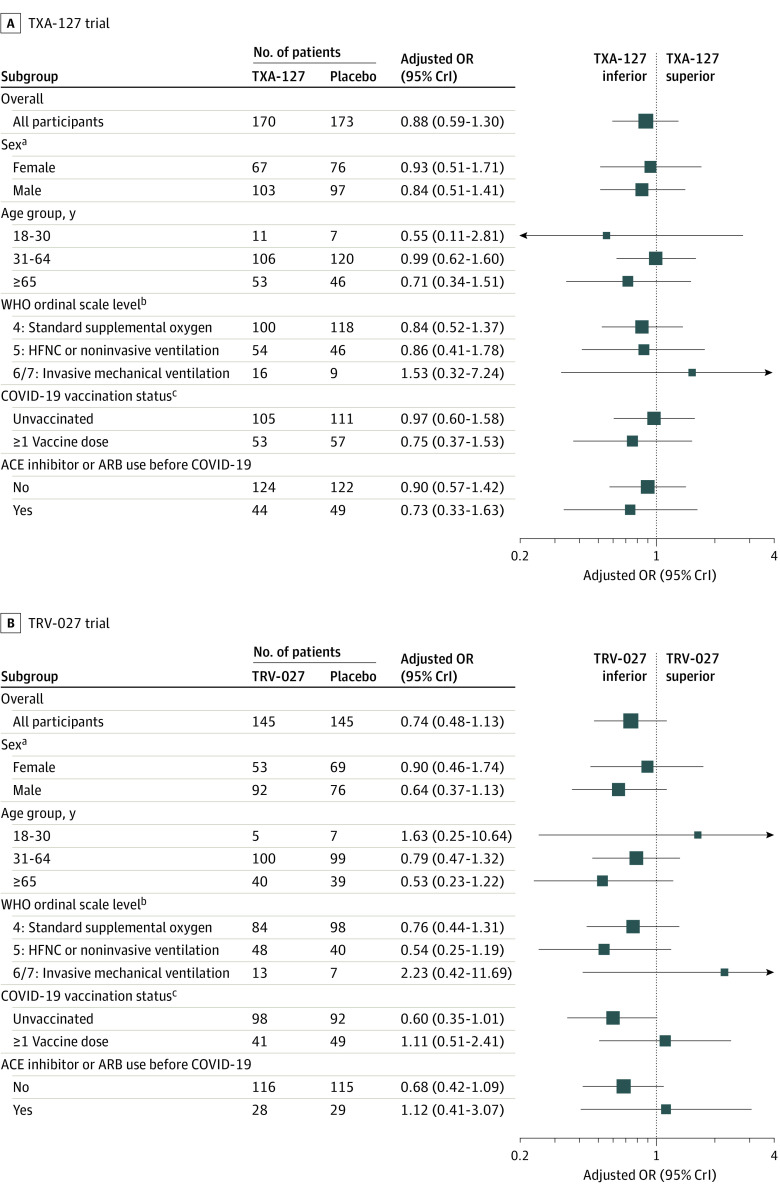
Figure 3. Primary Outcome of Oxygen-Free Days by Baseline Characteristics in the TXA-127 Trial and in the TRV-027 Trial.
ACE indicates angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CrI, credible interval; HFNC, high-flow nasal cannula; OR, odds ratio; and WHO, World Health Organization. The ORs were adjusted for sex, age group, and baseline WHO ordinal scale level. An oxygen-free day was calculated as 28 minus the number of days between randomization (day 0) and liberation from new supplemental oxygen use during the 28 days. Patients who died before day 28 were coded as having −1 oxygen-free days (worst possible outcome). The subgroup analyses of oxygen-free days included patients with partially observed data (only known to be within a certain range). Additional information appears in eTables 11 and 12 in Supplement 1, including the number of patients with partially observed oxygen-free days.
aNot prespecified as a subgrouping variable; thus, heterogeneity of treatment effect by sex is a post hoc analysis.
bThe WHO COVID-19 clinical progression scale is an 8-level ordinal scale representing the worst patient clinical status on a given day. The descriptions for levels 1-8 appear in footnote d in Table 1.
cPatients with unknown vaccination status were excluded (17 patients in the TXA-127 trial and 10 patients in the TRV-027 trial).