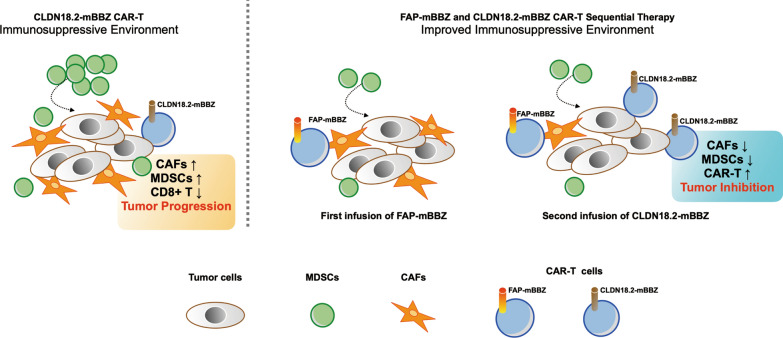
Fig. 7.
Schema: Sequential Therapy enhances the antitumor ability of CAR-T by suppressing the infiltration of MDSCs. Left: CAFs are crucial in TME, forming an immune surveillance barrier and perpetuating tumor-promoting. The CAFs could also promote recruit monocytes from the bone marrow, such as MDSCs, to form a tumor-suppressing microenvironment, suppressing CAR-T cell function. Right: FAP-targeted CAR-T cells eliminate CAFs via specific recognition of FAP on CAFs in the tumor microenvironment. Further, CLDN18.2-targeted CAR-T cells could also increase cytotoxic T cells and inhibit the recruiting of MDSCs. With an improved immune suppressive microenvironment, the antitumor effect of the sequential infusion of CLDN18.2-targeted CAR-T cells were enhanced