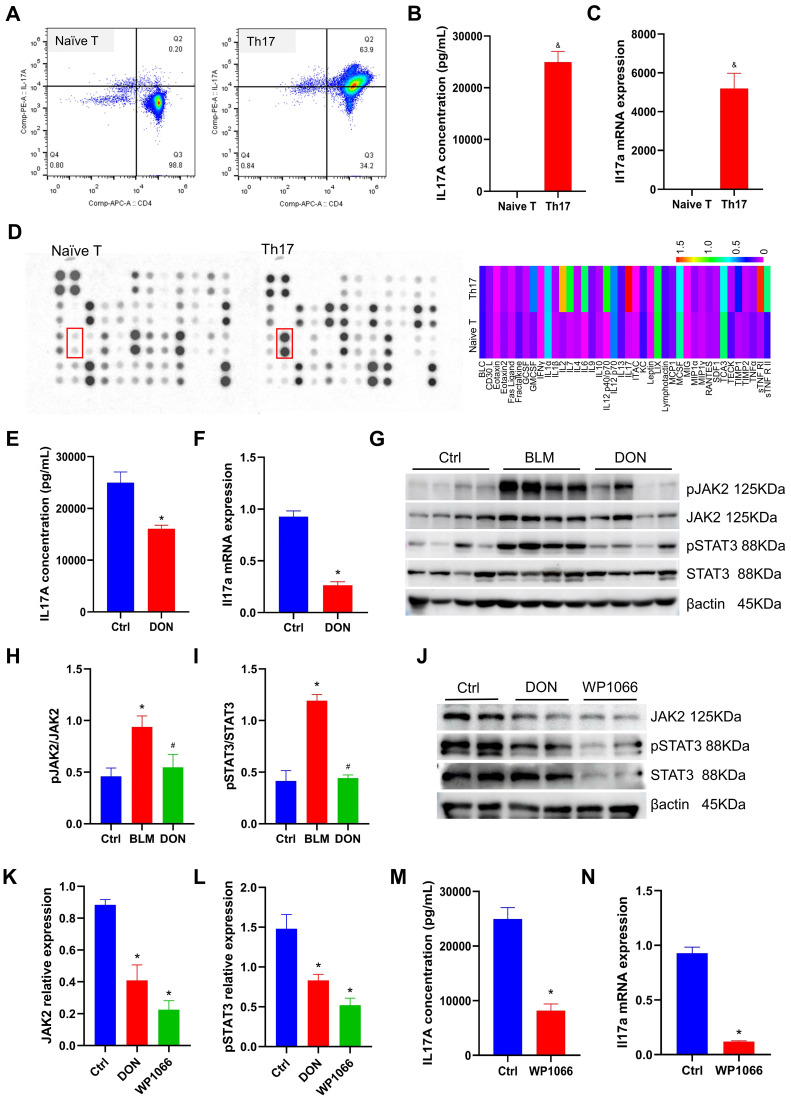
Figure 5.
DON regulates Th17 differentiation by inhibiting JAK2-STAT3 pathway. A. Flow cytometry to detect naïve T lymphocytes differentiating into Th17 cells. B. Quantitative analysis of IL17A levels in Th17 differentiation medium (n = 5). C. Quantitative analysis of Il17a mRNA expression (n = 4). D. Mouse inflammation antibody array-membrane to detect inflammatory factors and cytokines in Th17 differentiation medium and heat map show the grayscale values. E. Quantitative analysis of IL17A levels after DON treatment (n = 5). F. Quantitative analysis of Il17a mRNA expression after DON treatment (n = 4). G. Representative protein levels in lung tissue. H~I. Statistical analysis of the levels of pJAK2 and pSTAT3 in lung tissue (n = 8). J. Representative protein levels in Th17 cells. K~L. Statistical analysis of the levels of JAK2 and pSTAT3 in Th17 cells (n = 4). M. Quantitative analysis of IL17A levels in Th17 cells after WP1066 treatment (n = 5). N. Quantitative analysis of Il17a mRNA expression in Th17 cells after WP1066 treatment (n = 4). Ctrl: control, BLM: bleomycin, DON: donepezil, IL17A: interleukin 17A, JAK2: Janus Kinase 2, STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Th17: T helper 17. *P < 0.05, versus Ctrl group, #P < 0.05, versus BLM group, &P < 0.05, versus Naïve T cells group.