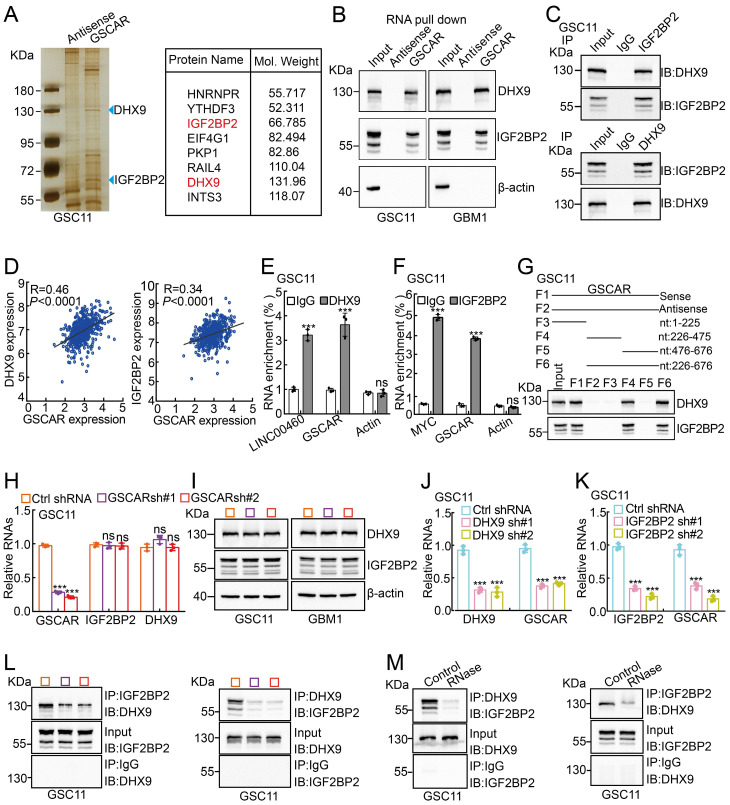
Figure 6.
GSCAR facilitated the interaction between DHX9 and IGF2BP2. (A) Silver staining for biotinylated GSCAR-interacting proteins was followed by mass spectrometry analysis. Blue arrowheads indicate the candidate differentially identified proteins. (B) The interactions between GSCAR, DHX9, and IGF2BP2 were verified by RNA pull-down assay followed by immunoblot detection of the indicated proteins in GSC11 and GBM1 cells. Biotin-labeled GSCAR and its antisense RNA were transcribed in vitro using T7 RNA polymerase. β-Actin was used as a negative control. (C) The interaction between DHX9 and IGF2BP2 was examined by immunoprecipitation assay in GSC11 cells. (D) The correlations between DHX9/IGF2BP2 and GSCAR expression were examined using the TCGA-LGG dataset with Pearson's correlation analysis. (E-F) The protein-RNA interaction was verified by RIP assay in GSC11 cells. LINC00460, β-actin, or c-MYC was used as reciprocal control. (G) The RNA-protein interaction fragments were identified using serial truncated forms of GSCAR by RNA pull-down assay. Immunoblotting was performed using the indicated antibodies. (H-I) Effect of GSCAR knockdown on the expression of IGF2BP2 and DHX9 in GSC11 cells, as assessed by RT-PCR and immunoblot assays. (J-K) The relative RNA expression levels of the indicated genes were examined by RT-PCR. (L-M) Depleting GSCAR by shRNA (L) or RNase treatment (M) markedly reduced the interaction between DHX9 and IGF2BP2. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.