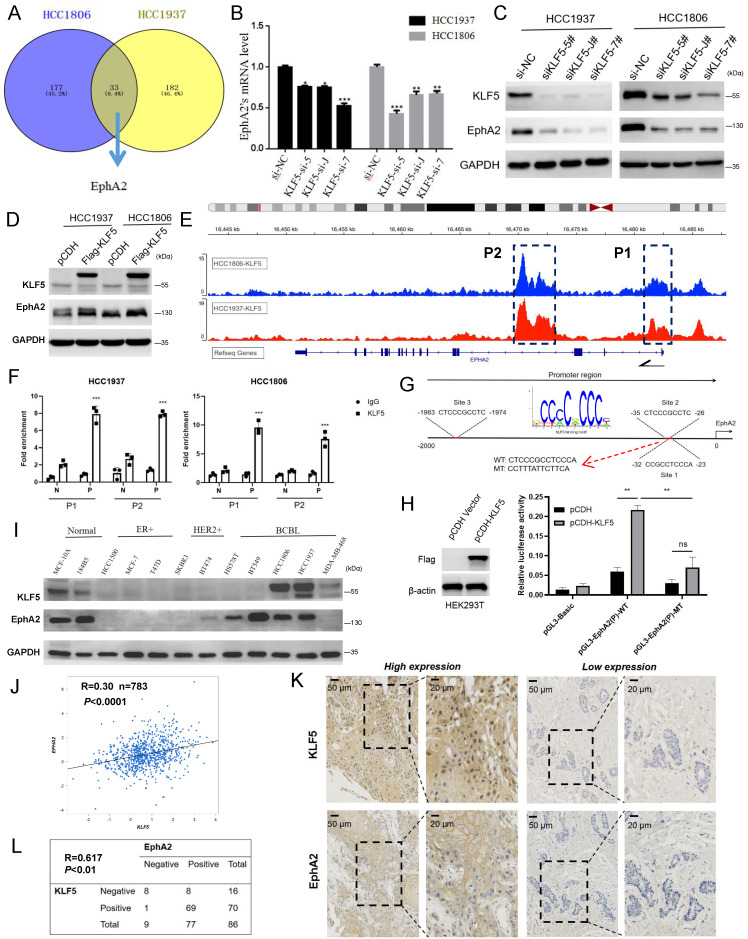
Figure 2.
KLF5 positively regulates EphA2 expression in BLBC. (A) Knockdown of KLF5 in HCC1937 and HCC1806 cells for RNA-seq and 33 genes were found to be positively regulated by KLF5, including EphA2. (B-C) Knockdown of KLF5 was confirmed to suppress EphA2 expression by RT‒qPCR and WB assay; (D) Overexpression of KLF5 promotes EphA2 expression by WB assay; (E) ChIP-seq results of KLF5 in HCC1937 and HCC1806 cells showed two potential binding sites of KLF5 in the EphA2 gene locus, which were named P1 and P2, respectively; (F) Validation of KLF5 binding sites P1 and P2 in the EphA2 gene by ChIP‒qPCR in HCC1937 and HCC1806, respectively. P (Positive) or N (Negative) is the primer targeting P1/P2 or distant non-peak sequence, respectively. G. JASPAR database analysis of the KLF5 binding motif and potential binding sites of KLF5 in the promoter region of EphA2 (Site 3 is out of P1/P2 and Sites 1/2 share common motif); (H) Luciferase activity assay for detecting the transcriptional activity of WT and mutated promoters of EphA2 in HEK293T cells in the absence or presence of KLF5 overexpression. (I) In multiple breast cancer cell lines and normal breast epithelial cell lines, a WB assay found a certain trend of coexpression of KLF5 and EphA2; (J) Database (bc-GenExMiner v4.9) analysis revealed a correlation between the mRNA expression of EphA2 and KLF5 in BLBC patients (n=783) (R=0.3); (K-L) Detection by tissue microarray in 86 cases revealed that EphA2 and KLF5 were both highly expressed in BLBC and that their expression was positively correlated.