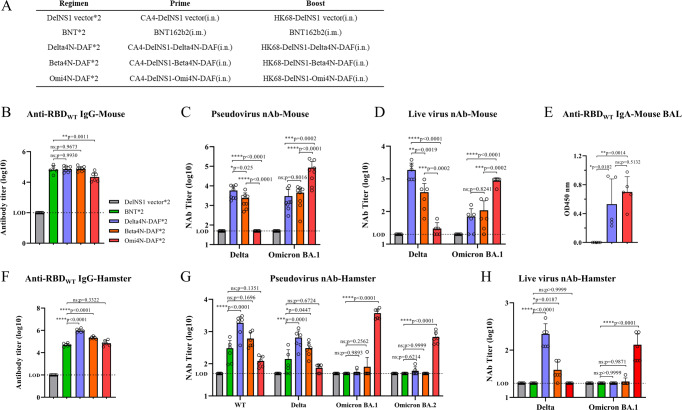
Fig. 2. Immunogenicity of DelNS1-RBD4N-DAF LAIVs in mice and hamsters.
A Prime-boost immunization regimen and grouping of BALB/c mice and hamsters. BALB/c mice were prime-boost immunized intranasally with 2 × 106 pfu of Delta4N-DAF, Beta4N-DAF, DelNS1-RBD4N-DAF with Omicron BA.1 RBD (Omi4N-DAF) or DelNS1 vector only control, or through intramuscular injections of the BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine (BNT, 5ugand sera collected 14 days after the second immunization for testing of anti-S1 RBD-specific IgG titers (B) (Delta4N-DAF (n = 8 mice), Beta4N-DAF (n = 8 mice), Omi4N-DAF (n = 6 mice), DelNS1 vector (n = 8 mice), BNT (n = 5 mice)). C Neutralization titers against pseudotyped viruses displaying Delta or Omicron BA.1 spike proteins (n = 8 mice for each group), and (D) neutralization titers against live SARS-CoV-2 variants (Delta and Omicron BA.1) (n = 6 mice for each group). E The bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) of mice was collected 10 days after boost immunization and anti-S1 RBD-specific IgA titers determined (n = 5 mice for each group). Syrian hamsters were prime-boost immunized intranasally with either 5 × 106 pfu of Delta4N-DAF, Beta4N-DAF, Omi4N-DAF, or DelNS1 vector only control, or through intramuscular injections of the BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine (5ug). F Sera samples were collected 14 days after the second immunization and tested for anti-S1 RBD-specific IgG titers (n = 6 hamsters for each group). G Neutralization titers against pseudotyped viruses with wild type, Delta or Omicron spike proteins (n = 6 hamsters for each group), and (H) neutralization titers against live SARS-CoV-2 variants (Delta and Omicron) (n = 6 hamsters for each group). LOD lower limit of detection. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Numerical labels indicate means. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test: ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, ns not significant.