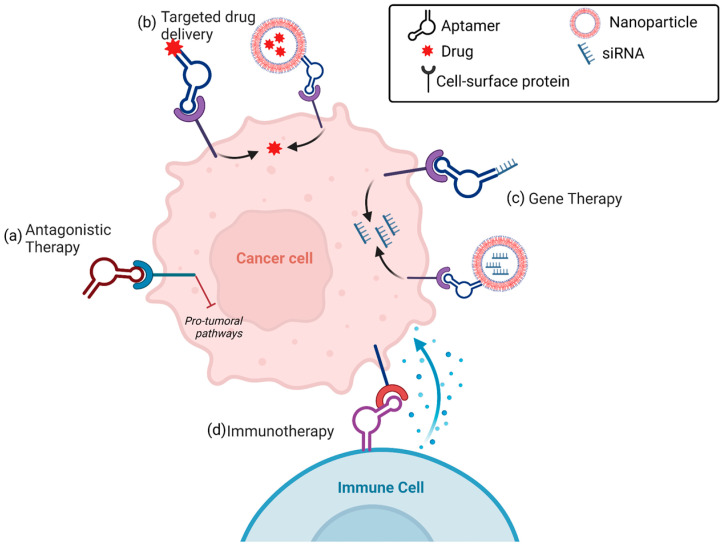
Figure 2.
Aptamer-based anticancer therapy. (a) Antagonistic therapy: aptamers bind to cancer cell surface targets, inhibiting protumoral pathways. (b) Targeted drug delivery: aptamers conjugated to drug-loaded nanoparticles or linked to drugs bind to cell surface targets and internalize into cancer cells, resulting in selective intracellular drug delivery. (c) Gene therapy: aptamers decorating small-interfering RNA (siRNA)-loaded nanoparticles or conjugated directly to siRNA, bind to cell surface targets and internalize into cancer cells, resulting in selective gene silencing. (d) Immunotherapy: aptamers stimulate immune cells against cancer cells (see text for details). Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 2 March 2023).