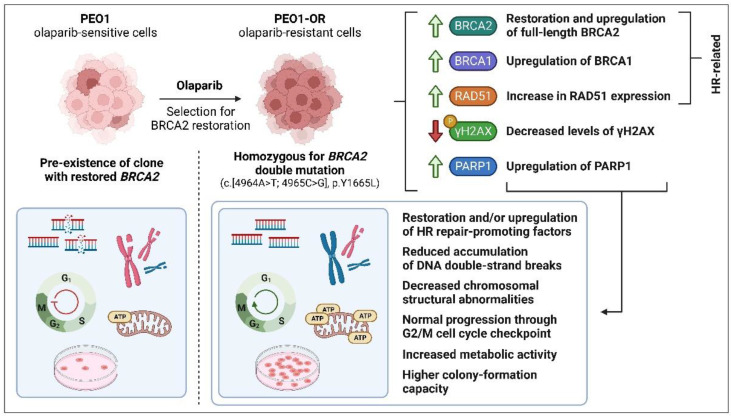
Figure 10.
Co-existing mechanisms conferring resistance to olaparib in PEO1-OR BRCA2MUT HGSOC cells. PEO1-OR cells underwent selection for BRCA2 restoration following prolonged treatment with olaparib, which led to enrichment in sub-dominant clones present in parental cells harboring the BRCA2 double mutation (c.[4964A > T; 4965C > G], p.Y1655L) removing the premature termination codon. Upregulation of BRCA2, BRCA1, RAD51, and PARP1, along with a concurrent decrease in γH2AX levels, contributed to decreased sensitivity to olaparib.