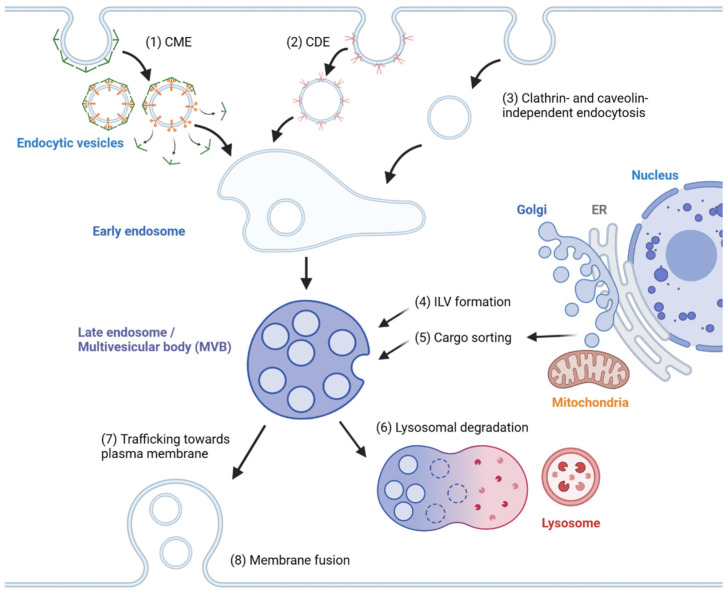
Figure 1.
Overview of exosome biogenesis. Endocytic vesicles are generated by (1) clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME), (2) caveolin-dependent endocytosis (CDE) and (3) clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytosis. After the fusion of endocytic vesicles to form early endosomes, (4) ILVs are generated by ESCRT-dependent and ESCRT-independent pathways, resulting in the formation of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). (5) Cargoes are sorted into ILVs from various organelles, including the trans-Golgi network (TGN), endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria. (6) MVBs can then fuse with lysosomes and undergo lysosomal degradation. (7) Alternatively, MVBs are trafficked towards the plasma membrane and (8) undergo membrane fusion for the extracellular release of ILVs as exosomes.