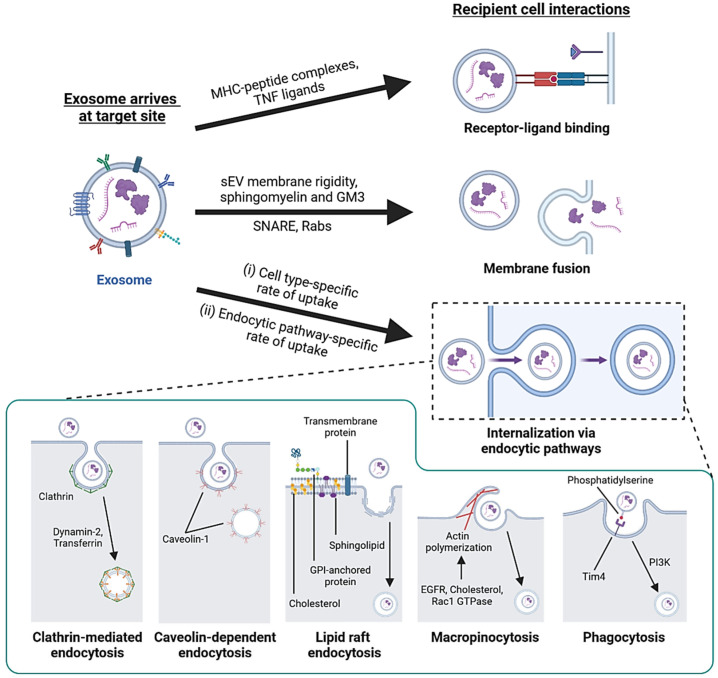
Figure 4.
Interactions of exosomes with recipient cells. Exosomes carrying MHC–peptide complexes or TNF ligands undergo receptor–ligand interaction with recipient cells to activate immune cells or trigger apoptosis in cancer cells. Exosomes that have high membrane rigidity and enrichment in sphingomyelin and GM3 have increased fusion efficiency. SNARE and Rab proteins are required for membrane fusion. Most exosomes are taken up by internalization. Different cell types differ in overall exosome uptake efficiency, and each cell may use more than one endocytic pathway for exosome uptake in parallel. Endocytic pathways, such as clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME), caveolin-dependent endocytosis (CDE), lipid raft endocytosis, macropinocytosis and phagocytosis, contribute to exosome uptake.