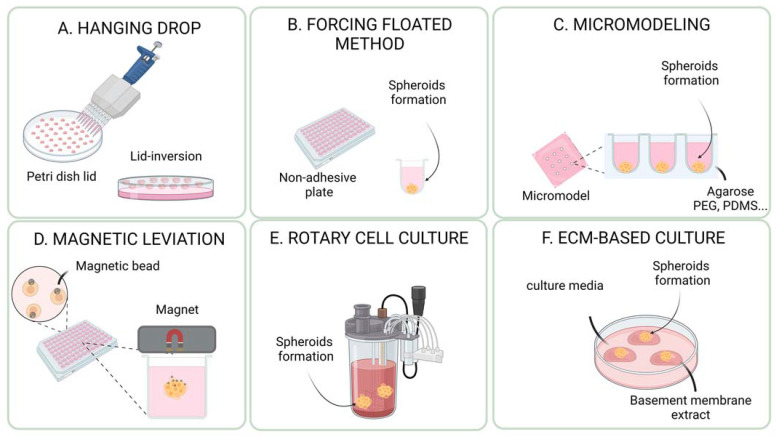
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the different 3D cell culture techniques: (A) In the hanging method, the cells form a single spheroid by accumulating at the free liquid interface formed by their suspension due to the inversion of the dish. (B) The forced floating method can be carried out using uncoated polystyrene plates or plates coated with a hydrophilic polymer that suppresses cell-substrate interactions, e.g., ultra-low attachment (ULA) plates. (C) In the modeling culture system, the cells are seeded and allowed to self-aggregate into non-adhesive micro-molds. (D) The magnetic levitation employed magnetic beads assembly technique. Cells treated with magnetic beads aggregate into spheroids or organoids under magnetic forces within a few hours after a magnet is placed on top of the lid. (E) The Rotary Cell Culture System is another agitation-based technique used to obtain a higher number of large spheroids with a small number of starting cells. (F) Organoids can be cultured in the submerged method by disrupting tissue mechanically and enzymatically into single-cell suspensions, followed by embedding them in basement membrane extract (BME) and submerging them in the culture media. This figure was created with BioRender.com (accessed on 14 March 2023).