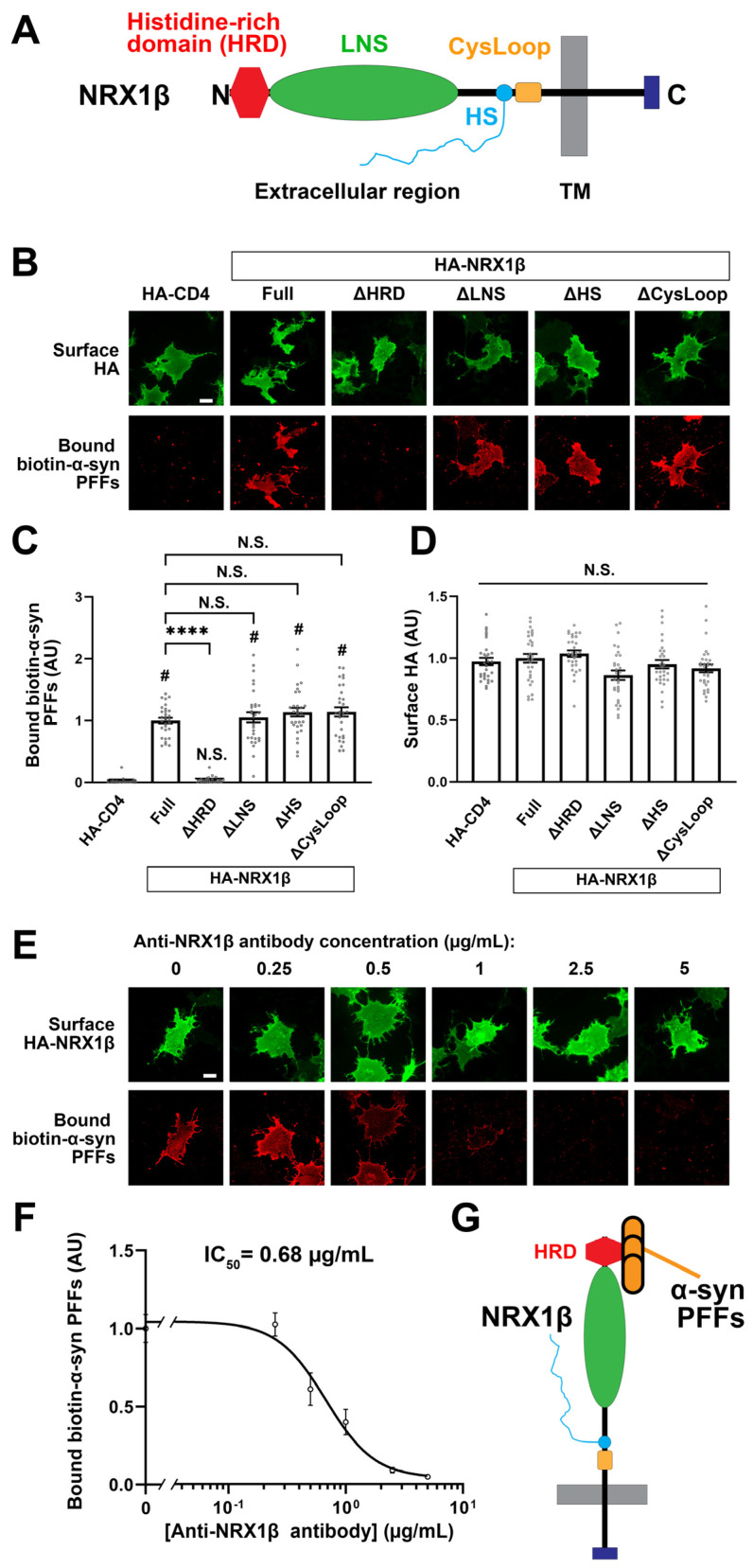
Figure 5.
The N-terminal histidine-rich domain (HRD) of NRX1β is responsible for the binding of α-syn PFFs to NRX1β. (A) A diagram showing the domain structure of NRX1β. HRD: the histidine-rich domain (HRD), LNS: laminin-neurexin-sex hormone binding globulin, HS: a heparan sulfate modification site, CysLoop: cysteine loop region, TM: transmembrane region, N and C: N- and C-terminals, respectively. (B) Representative images showing the binding of 1 μM biotin-α-syn PFFs to COS-7 cells expressing the indicated HA-NRX1β deletion constructs, full-length HA-NRX1β (Full) or HA-CD4, a negative control. NRX1β lacking the HRD (ΔHRD) has no binding of biotin-α-syn PFFs. The binding of biotin-α-syn PFFs to NRX1β lacking either the LNS, the HS or the CysLoop (ΔLNS, ΔHS, ΔCysLoop) appears comparable to the binding to full-length NRX1β. Scale bar: 30 μm. (C) Quantification of the average intensity of bound biotin-α-syn PFFs on COS-7 cells expressing the indicated HA-NRX1β constructs. Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001. # p < 0.0001 compared with HA-CD; **** p < 0.0001 compared with HA-NRX1β Full by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. N.S., not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (n = 30 cells for each of three independent experiments). (D) Quantification of the average intensity of surface HA on COS-7 cells expressing the indicated HA-NRX1β constructs in (C). Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA, p = 0.0034. N.S., not significant in the comparisons with HA-CD4 and HA-NRX1β Full. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (n = 30 cells for each from three independent experiments). (E) Representative images of cell surface protein binding assays showing COS-7 cells expressing HA-NRX1β co-treated with 1 μM biotin-α-syn PFFs and a mouse monoclonal antibody against the HRD of NRX1β (anti-NRX1β antibody) at varying concentrations (0–5 μg/mL). Co-treatment with anti-NRX1β appears to inhibit the binding of α-syn PFFs to COS-7 cells expressing HA-NRX1β in a dose-dependent manner. Scale bar: 30 μm. (F) Quantification of biotin-α-syn PFFs (1 μM monomer equivalent) bound to COS-7 cells expressing HA-NRX1β in the presence of various concentrations of anti-NRX1β antibody (0–5 μg/mL). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.68 μg/mL. (G) A diagram showing that α-syn PFFs bind to NRX1β through its HRD.