Fig. 1.
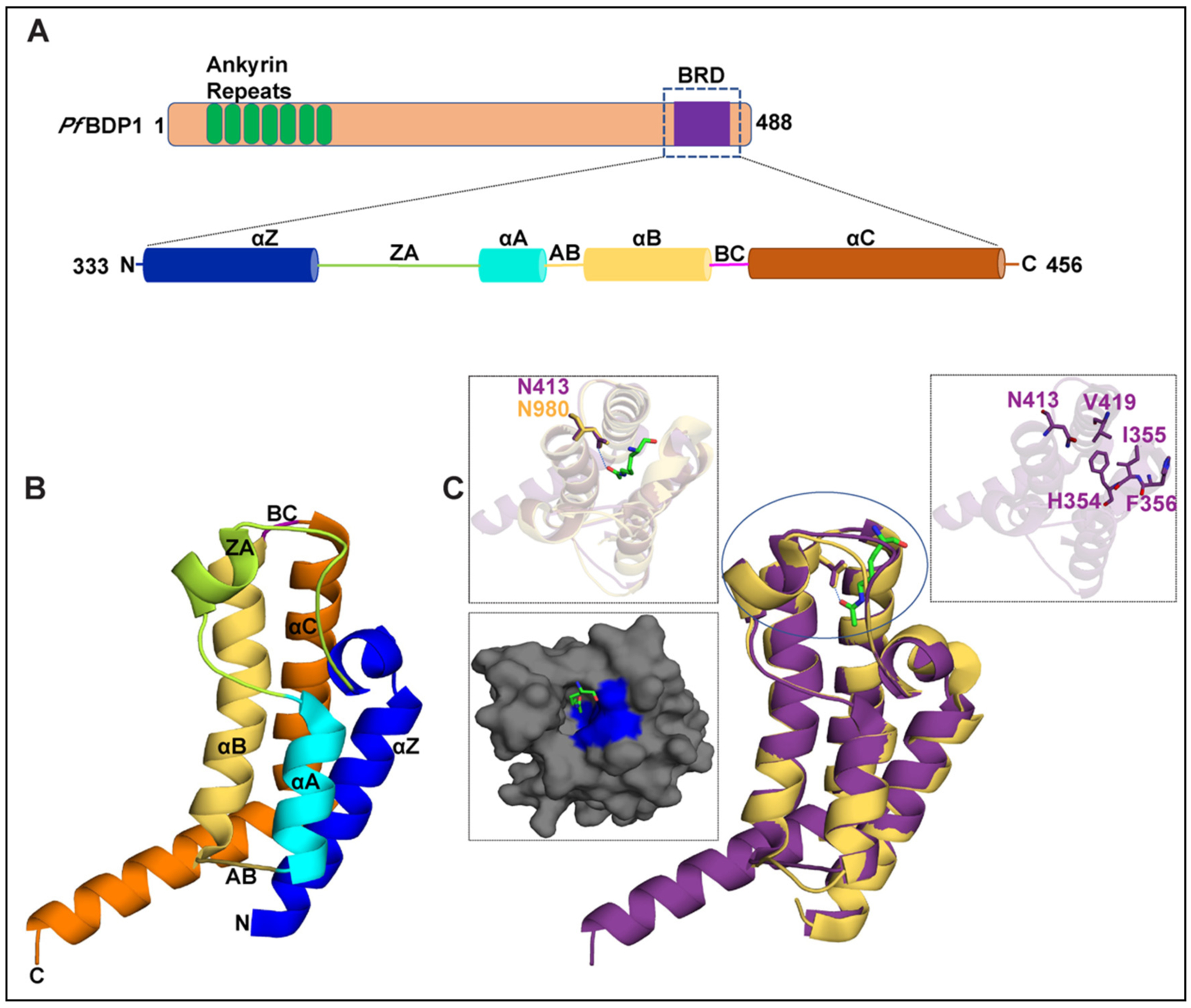
Structural features of the PfBDP1 protein. (A) Domain organization of PfBDP1 protein, where the ankyrin repeats are highlighted in green, loop regions in tan, and the bromodomain (BRD) in purple. The BRD is further expanded to highlight the secondary structure elements assigned to regions of the amino acid sequence based on the 2.0 Å crystal structure of the PfBDP1-BRD (333–456) (PDB ID: 7M97). (B) Cartoon representation of the PfBDP1-BRD (333–456) (PDB ID: 7M97) structure, where the αZ helix is blue, the αA helix is cyan, αB helix is yellow, αC helix is orange, the ZA loop is green, and the BC loop is magenta. (C) Structural alignment of PfBDP1-BRD (333–456) in purple with the TIF1α bromodomain (PDBID: 3O35) in yellow. The acetyllysine found in the TIF1α bromodomain is colored green and represented as a stick model. The left panel insert shows a zoomed in view of the binding pockets and coordination of acetyllysine by the TIF1α bromodomain. The surface representation of the predicted binding pocket of PfBDP1-BRD (333–456) is shown below where the hydrophobic residues are highlighted in blue and the acetyllysine group from the overlaid TIF1α bromodomain structure is in green. The right panel insert shows the PfBDP1-BRD structure in purple with the conserved asparagine N413, the gatekeeper residue V419, and the HIF motif (354–356 aa) residues depicted as sticks.
