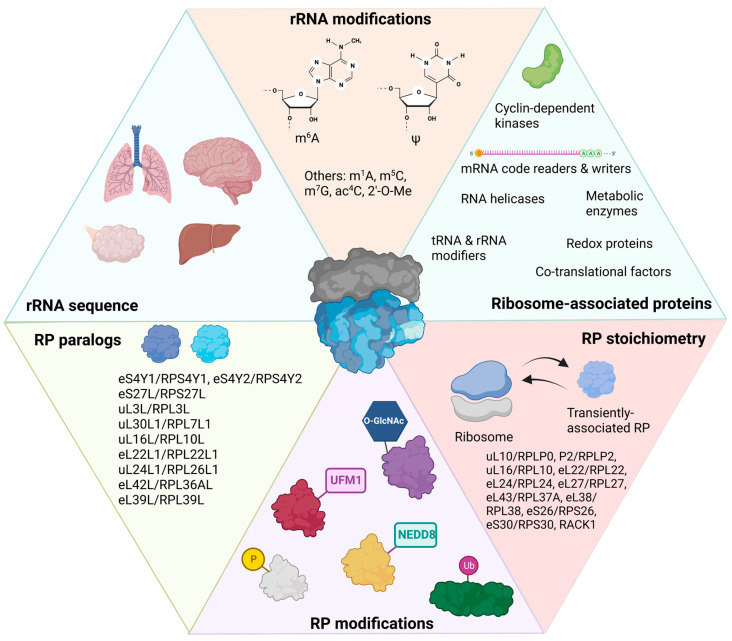
Figure 1.
Ribosomal heterogeneity in mammals. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) contains tissue-specific sequences (blue panel). There are several rRNA modifications, including N6-methyladenosine (m6A), N1-methyladenosine (m1A), pseudouridine (Ψ), 5-methylcyosine (m5C), N7-methylguanosine (m7G), N4-acetylation of cytosine (ac4C), and 2′-O-methylation (2′-O-Me) (orange panel). Multiple factors associate with ribosomes, altering their translational capacities (green panel). Ribosomal protein (RP) abundance can affect ribosome stoichiometry, and some RPs are known to be incorporated into ribosomes outside of canonical ribosome biogenesis in neurons (red panel). RPs can also contain several post-translational modifications: “P” is phosphorylation; “Ub” is ubiquitin protein; “UFM1” is ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 protein; “NEDD8” is neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8 protein, a Ub-like protein; and “O-GlcNAc” is O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (purple panel). Nine canonical RPs also have paralogous proteins, some of which are tissue specific (yellow panel). This figure was created with BioRender.com.