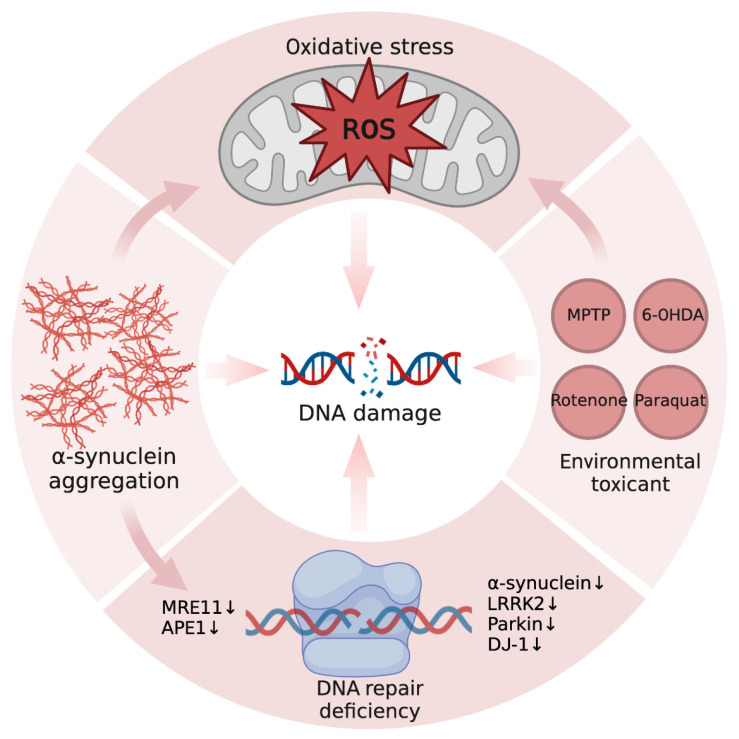
Figure 1.
Sources of DNA damage in PD. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can directly attack genomic DNA, causing many types of DNA damage. Pathogenic α-synuclein can damage DNA indirectly through ROS or directly cleave DNA, leading to DNA strand breakage. On the other hand, α-synuclein can also cause DNA repair defects by affecting the expression of DNA repair proteins, including MRE11 and APE1. Recent studies have highlighted the role of PD-causing proteins in DNA repair, including endogenous α-synuclein, LRRK2, parkin, and DJ-1, which partially explains the cause of abnormal DNA repair and damage accumulation in PD. Finally, environmental toxicants, an important component in the pathogenesis of sporadic PD, can also induce genomic DNA damage and lead to DNA damage-dependent dopaminergic neuron death. The pink arrows in the figure represent causal effects, and the black arrows indicate downregulation of protein expression. (Created with BioRender.com).