Figure.
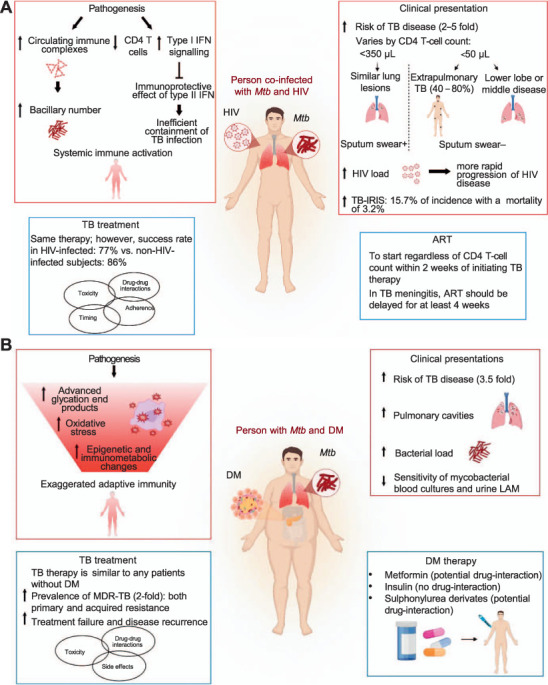
Schematic overview of the pathogenesis, clinical presentations and treatments in subjects with TB and HIV or DM. A) Subjects co-infected with Mtb and HIV are characterised by a systemic immune activation and show an increased risk for TB disease, HIV viral load and incidence of TB-IRIS. The appearance and location of pulmonary lesions vary according to the CD4 T-cell count. Treatment of TB-HIV co-infected individuals has a reduced success rate. ART should be started regardless of CD4 T-cell count and delayed in case of TB meningitis. B) TB-DM patients exhibit an enhanced adaptive immune response compared to those without DM, as well as an increased risk for TB, number and size of pulmonary cavities, and bacterial load. TB patients with DM have a higher risk for multidrug resistance and treatment failure. IFN = interferon; Mtb = M. tuberculosis; IRIS = immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; ART =antiretroviral therapy; LAM = lipoarabinomannan; DM = diabetes mellitus; MDR-TB = multidrug-resistant TB.
