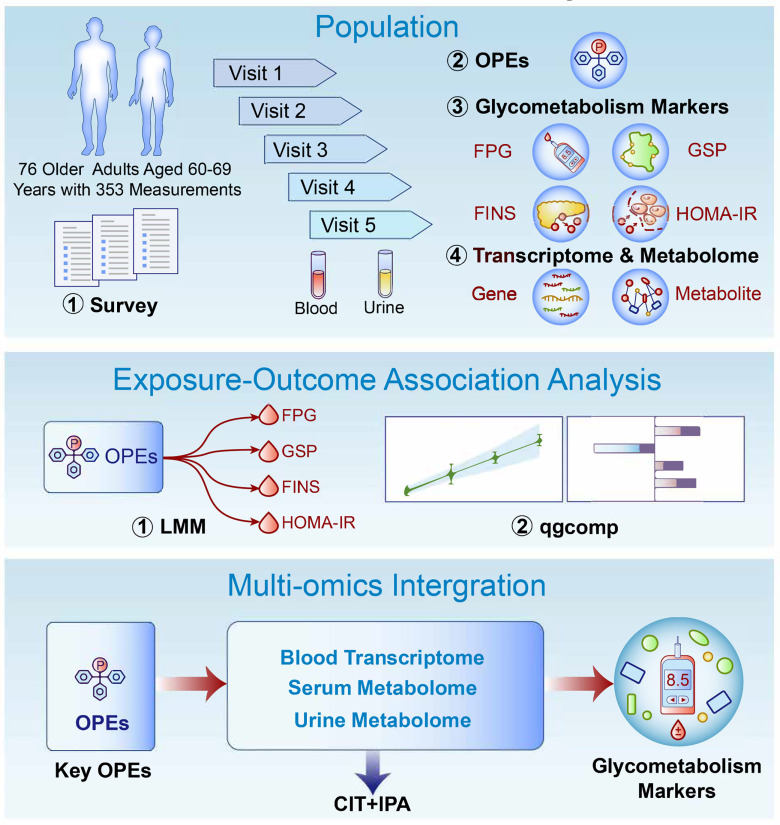
Figure 1.
Overview of the study design. Diagram of the present study design. Internal OPE exposure of 76 healthy older Chinese adults 60–69 years of age with five monthly longitudinal sample (blood and urine) collections was characterized previously. Glycometabolic markers (FPG, GSP, FINS, and HOMA-IR) were measured, and multi-omics profiling (peripheral blood transcriptome, serum metabolome, and urine metabolome) was conducted. Exposure–health outcome associations and multi-omics integrative analyses were further used to identify the key OPEs and to interpret the biological mechanisms underlying the perturbations of glycometabolic markers, respectively. Note: CIT, causal inference test; FINS, fasting insulin; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; GSP, glycated serum protein; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; IPA, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis; LMM, linear mixed-effects model; OPE, organophosphate ester; qgcomp, quantile g-computation.