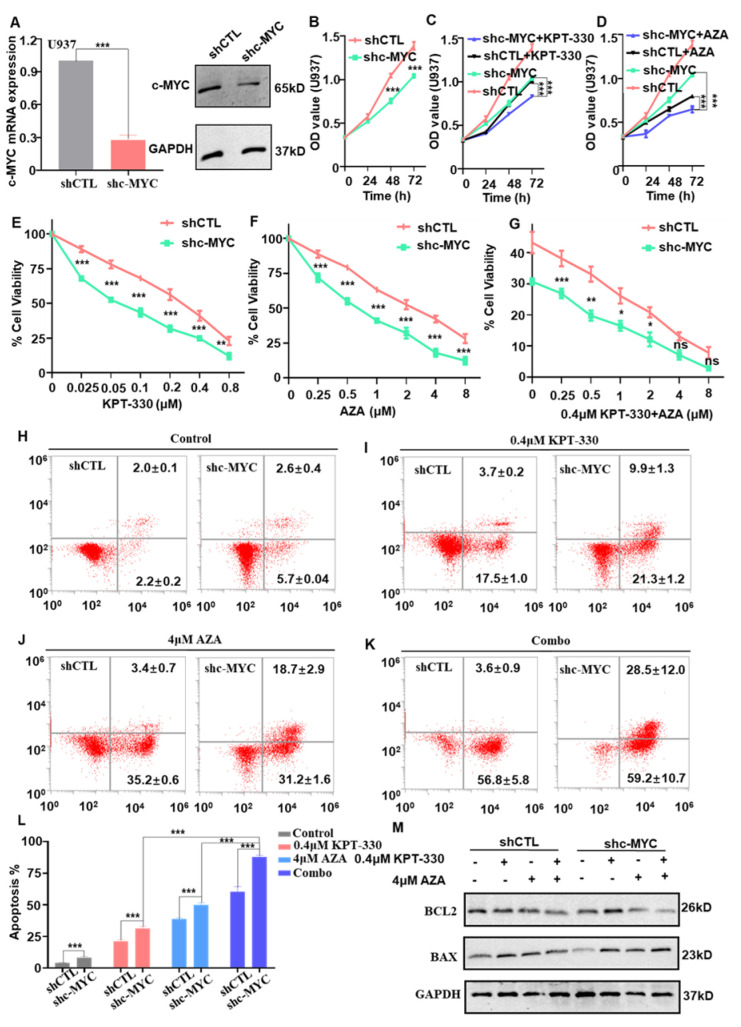
Figure 4.
Effect of c-MYC knockdown on the combination-mediated proliferation in U937 cells. (A) c-MYC was efficiently knocked down in the U937 cell by qPCR and western blot. (B) c-MYC knockdown (shc-MYC) inhibits cell proliferation arrest compared to that of scramble shRNA (shCTL) in U937 cells. (C,D) The effect of c-MYC knockdown by shRNA with XPO1 inhibitor or AZA on cell proliferation progression was analyzed by CCK-8 assay. Cells were treated with 0.1 μM KPT-330 or 1 μM AZA for 0–72 h for cell proliferation assay. (E–G) c-MYC knockdown facilitated the effect of KPT-330, AZA, and combo on cell proliferation arrest in U937 cells compared to shCTL. (H–K) The effect of shc-MYC facilitated the effect of KPT-330, AZA, and combo on cell apoptosis in U937 cells compared to shCTL. (L) The statistical chart shows the apoptosis effect of c-MYC knockdown by KPT-330, AZA, and combo in shCTL and shc-MYC cells. (M) Western blot data to show the changes of the apoptosis-related genes (BCL2 and BAX) in combo with shCTL and shc-MYC cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns: p > 0.05.