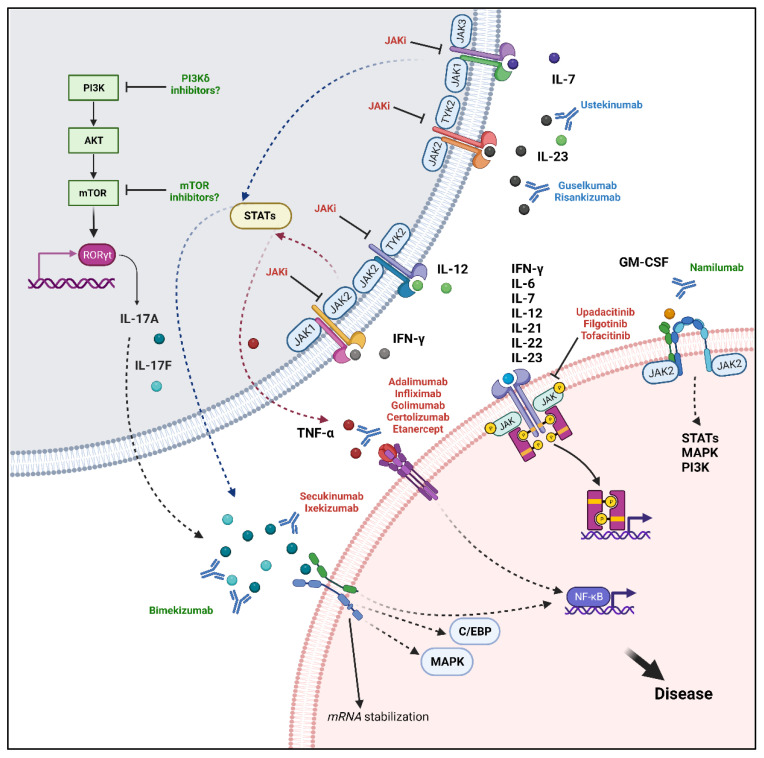
Figure 3.
Molecular targets and associated signalling pathways. Current therapeutic targets in axial-SpA include TNF-α, IL-17A, and JAKs. TNF-α signals mainly through the NF-κB pathway and could be inhibited by several monoclonal antibodies, anti-TNF-α, and the fusion protein etanercept. IL-17A has a pivotal role in mediating disease pathogenesis and could activate several pathways such as the canonical NF-κB, MAPK, C/EBP pathways and the alternative stabilization of mRNA. Secukinumab and ixekizumab can bind IL-17A with different affinities, inhibiting its downstream actions. The JAK inhibitors upadacitinib, filgotinib, and tofacitinib may act directly by blocking the signal transduction of proinflammatory cytokines including IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-7, IL-12, IL-21, IL-22, IL-23, or indirectly blocking TNF-α and IL-17A/F production following inhibition of upstream stimuli. New targets include the simultaneous inhibition of IL-17A and IL-17F with bimekizumab. Moreover, a potential therapeutic strategy may be represented by GM-CSF inhibition through namilumab. Finally, the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway has important immunomodulatory roles, it can elicit RORγT translocation into the nucleus, promoting IL-17A/F production and could be further investigated as a novel target. “Created with BioRender.com”.