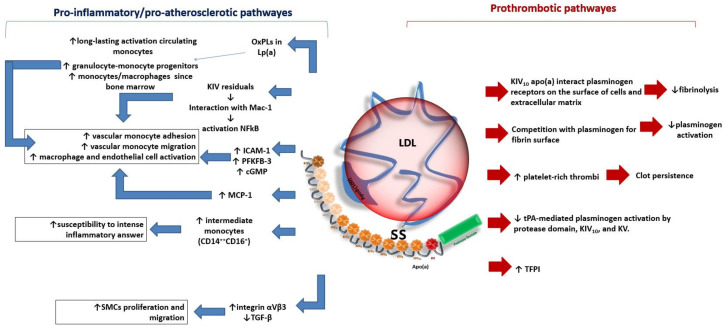
Figure 1.
The potential impact of lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) on atherosclerotic and thrombotic processes. The figure represents the main hypothetic mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and thrombosis in patients with higher Lp(a) serum concentrations. Apo(a): apolipoprotein(a); CD: cluster of differentiation; cGMP: guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate; ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion molecule-1; KIV: kringle IV; KV: kringle V; LDL: low density lipoprotein; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; NFkB: nuclear factor kB; OxPLs: oxidized phospholipids; PFKFB-3: 6-phophofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase enzyme; SMC: smooth muscle cell; TFPI: tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta; tPA: tissue plasminogen activator.