Figure 3.
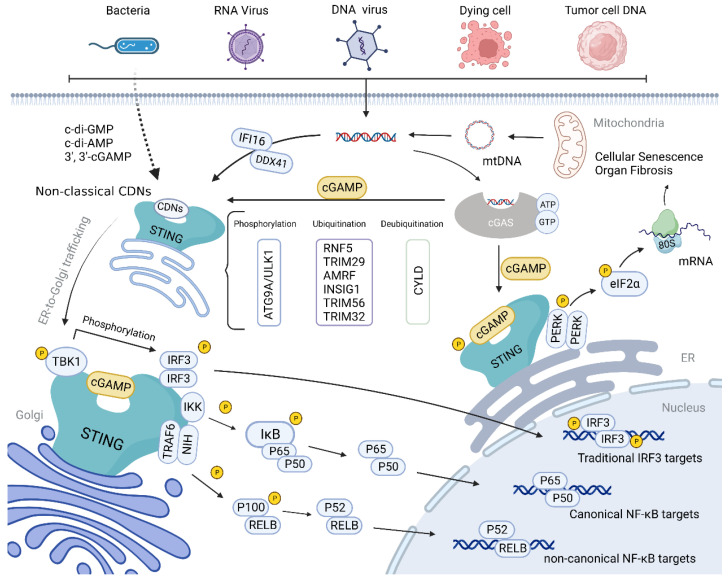
Schematic diagram of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. cGAS can recognize abnormally exposed cytoplasmic DNA molecules, including viral and bacterial DNA, DNA produced by the reverse transcription of RNA viruses, and DNA produced by self-cell damage. It can catalyze the synthesis of 2′, 3′-cGAMP, which specifically binds to STING dimer for oligomerization. After activation, STING is translocated to the Golgi via ERGIC, during which TBK1 and IRF3 are recruited, and this complex induces an immune response by phosphorylating IRF3 or NF-κB. In addition, STING can activate PERK and promote the phosphorylation of eIF2α, inducing translation program transformation. Autophagy, ubiquitination, recruitment inhibition, mutation, and other pathways can affect the STING pathway.