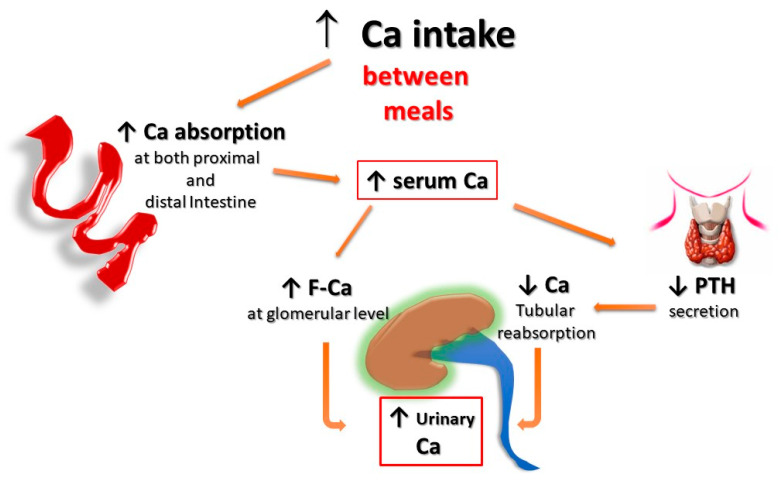
Figure 1.
Potential effects of Ca supplementation outside the meals on UL risk. The amount of calcium absorbed is greater when calcium supplements are given outside meals, as calcium cannot bind to dietary anions (phosphate, oxalate, sulphate, etc.), and this leaves room for intestinal absorption an increased amount of both calcium and unbound anions, resulting in increased urinary excretion of calcium, oxalate, and phosphate. F-Ca: filtered Calcium; PTH: Parathyroid Hormone.