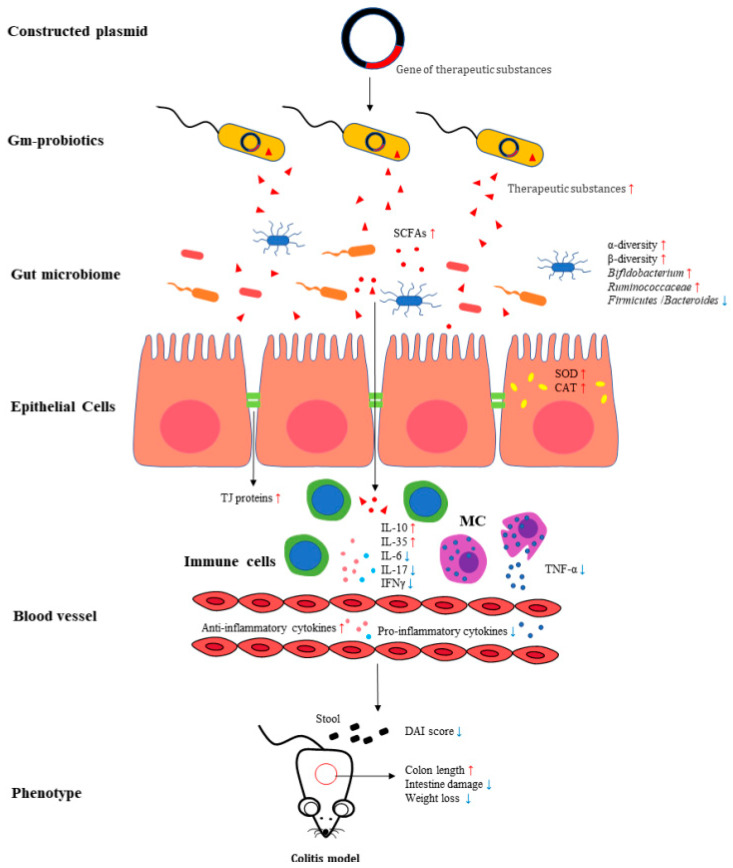
Figure 2.
The mechanism of gm probiotics involved in treating colitis models. Constructed plasmids containing genes for therapeutic substances are integrated into wild-type probiotics to treat colitis animal models by gavage or rectal administration. The gm probiotics ameliorated the clinical phenotypes of colitis, such as DAI score, body weight loss, and intestinal damages, via the mechanisms involved in improving gut microbiota, increasing the level of short-chain fatty acids, regulating immune cells, reducing expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines levels, and increasing the expression of tight junction proteins. (SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; MC: mast cells; TJ proteins: tight junction proteins; DAI: disease activity index).