Fig. 2.
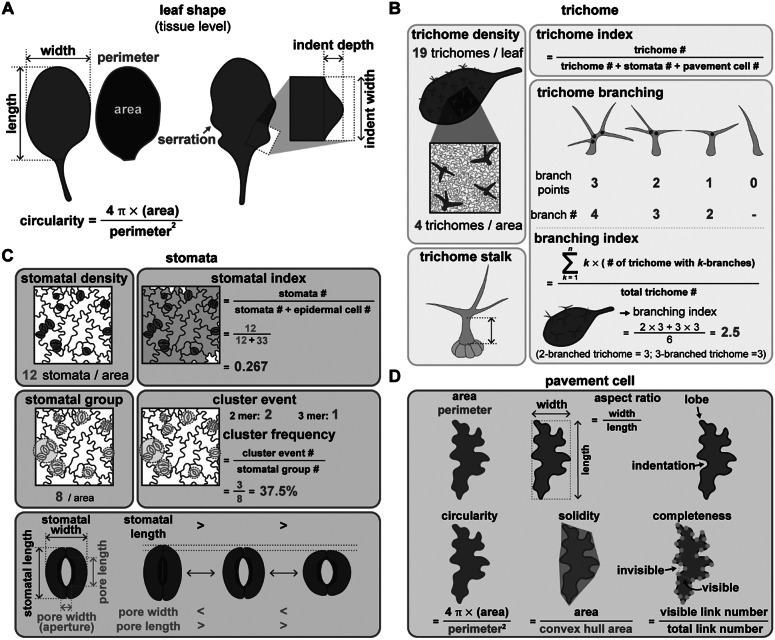
Quantitative methods to describe leaf morphology and the different types of epidermal cells. (A) Leaf shape can be described by its length, width, and the length/width ratio. Circularity calculated by (4
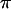 ×leaf area)/(square perimeter) indicates that the leaf shape is approximately round (circularity = 1) or contains serrations (circularity closer to 0). If serrations are visible on a leaf, the indent length and width can be used to describe the extent of serration. (B) Trichome phenotypes can be measured by the number of trichomes on a leaf and trichome morphology. Trichome density can be scored over an entire leaf or a given area. Trichome index is the number of trichomes divided by the number of total epidermal cells including trichome, stomatal, and pavement cells over a given area. The trichome stalk, the branching number, and the branching points can be used to represent trichome shape. The trichome branching index represents the average number of branches in a trichome population. (C) Stomatal phenotypes can be described by stomatal number, pattern, and dynamics. Stomatal density represents the number of stomata over a given area. The stomatal index is defined as the number of stomata divided by the total number of epidermal cells. Stomatal groups are the number of stomatal islands in a given area. Adjacent stomata are defined as one group. A cluster event represents the number of islands with adjacent stomata. Cluster frequency represents the error rate of forming stomatal clusters. The movements of stomata can be described by stomatal length and width. Pore length and width excluding guard cells may also be used. During stomatal opening, the stomatal and pore lengths decrease, while the pore width increases. (D) Pavement cell phenotypes can be described according to their shape including the parameters of area, perimeter, length and width. The aspect ratio calculates the ratio between cell length and width. The jigsaw-puzzle shape can be described by the number of lobes and indentations, which can be expressed as circularity, solidity, and completeness. Circularity is calculated as (4
×leaf area)/(square perimeter) indicates that the leaf shape is approximately round (circularity = 1) or contains serrations (circularity closer to 0). If serrations are visible on a leaf, the indent length and width can be used to describe the extent of serration. (B) Trichome phenotypes can be measured by the number of trichomes on a leaf and trichome morphology. Trichome density can be scored over an entire leaf or a given area. Trichome index is the number of trichomes divided by the number of total epidermal cells including trichome, stomatal, and pavement cells over a given area. The trichome stalk, the branching number, and the branching points can be used to represent trichome shape. The trichome branching index represents the average number of branches in a trichome population. (C) Stomatal phenotypes can be described by stomatal number, pattern, and dynamics. Stomatal density represents the number of stomata over a given area. The stomatal index is defined as the number of stomata divided by the total number of epidermal cells. Stomatal groups are the number of stomatal islands in a given area. Adjacent stomata are defined as one group. A cluster event represents the number of islands with adjacent stomata. Cluster frequency represents the error rate of forming stomatal clusters. The movements of stomata can be described by stomatal length and width. Pore length and width excluding guard cells may also be used. During stomatal opening, the stomatal and pore lengths decrease, while the pore width increases. (D) Pavement cell phenotypes can be described according to their shape including the parameters of area, perimeter, length and width. The aspect ratio calculates the ratio between cell length and width. The jigsaw-puzzle shape can be described by the number of lobes and indentations, which can be expressed as circularity, solidity, and completeness. Circularity is calculated as (4
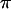 ×cell area)/(square perimeter). Solidity is the ratio between cell area and convex hull area. Completeness is the ratio between visible and total possible links. A visible link represents the link between two nodes without crossing over the cell outline. An invisible link is defined as a link between two nodes that crosses over the cell outline. All three parameters have maxima equal to 1. They decrease when the cell takes on the shape of a jigsaw-puzzle piece.
×cell area)/(square perimeter). Solidity is the ratio between cell area and convex hull area. Completeness is the ratio between visible and total possible links. A visible link represents the link between two nodes without crossing over the cell outline. An invisible link is defined as a link between two nodes that crosses over the cell outline. All three parameters have maxima equal to 1. They decrease when the cell takes on the shape of a jigsaw-puzzle piece.