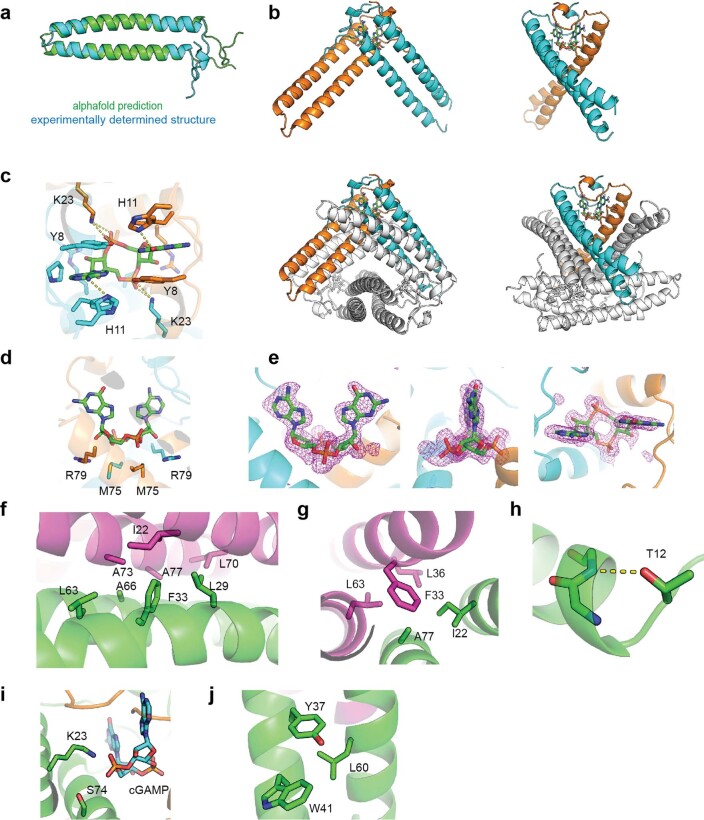
Extended Data Fig. 7. Structural analysis of the Vs.4:cGAMP complex.
a, Alignment of the alphafold predicted structure of the Vs.4 monomer that was used for molecular replacement and the experimentally determined structure of Vs.4 bound to cGAMP. b, A cartoon representation of a single cGAMP binding pocket formed by Vs.4 dimers with one chain colored orange and the other cyan. cGAMP is bound between these monomers (green sticks). Other monomers are colored white to display the dimer in the context of the larger hexameric structure. c, Detail of the hydrogen-bonds formed with cGAMP in the binding pocket of Vs.4. d, Additional interactions between Vs.4 and cGAMP in the binding pocket. e, Polder map for the cGAMP ligand, which was calculated with cGAMP with 5Å radius omitted. The difference density map is contoured 3.0σ with cGAMP superimposed. f, Hexamer interface with key residues highlighted. g–j, Residues found mutated in forward genetic screen shown in Extended Data Fig. 4a: A77I sterically clashes with the heximerization interface (g); T12I removes a stabilizing helix cap (h); S74N interferes with interactions with cGAMP (i); and the L60F may contribute to steric clashes (j).