Fig. 3. Vs.4 tightly binds and sequesters cGAMP.
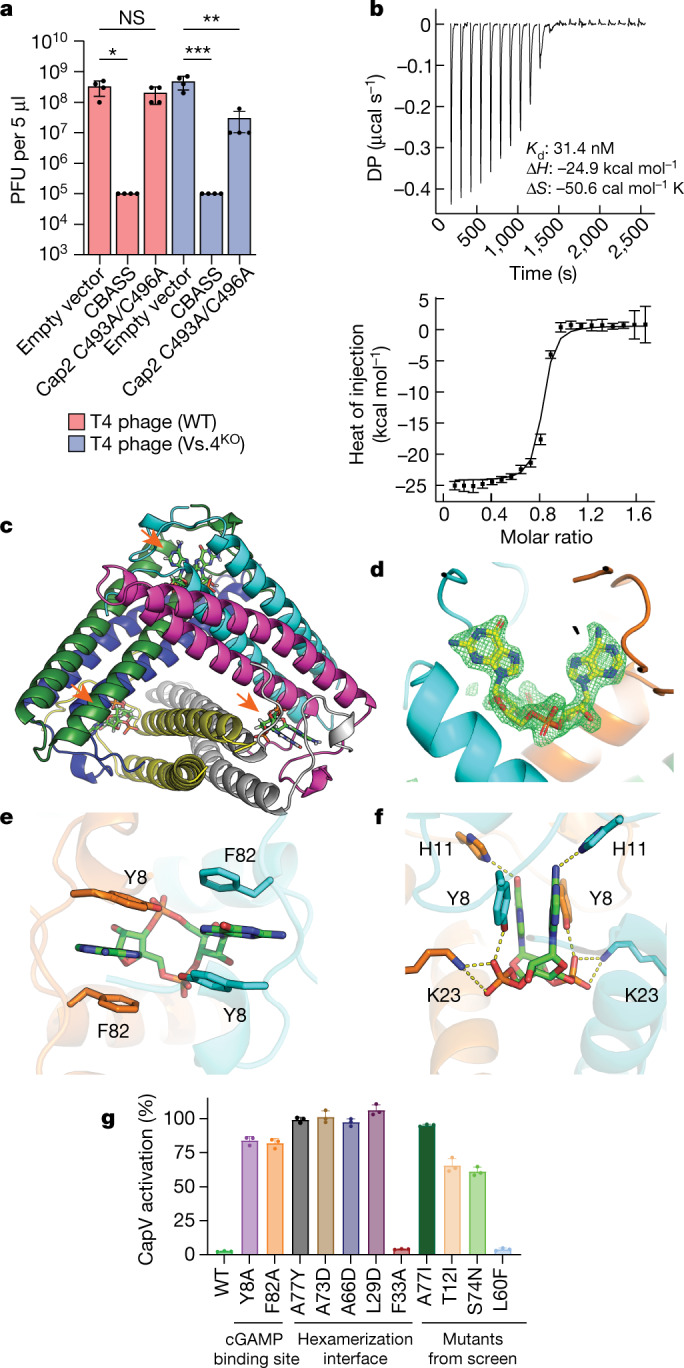
a, Viral titre of WT and Vs.4 knockout T4 phage in strains of E. coli MG1655 containing the WT or Cap2 C493A/C496A CBASS or empty vector. Bar graph represents average values ±s.e.m. of n = 4 independent experiments with individual points overlaid. NS, not significant, *P < 0.05 (P = 0.0178), **P < 0.005 (P = 0.0010) and ***P < 0.0005 (P = 0.0005) by one-way analysis of variance test. b, Representative example of a raw titration trace of differential power (DP) versus time (top) and integrated data (bottom, data points depict integrated heat of injection and error bars depict the weighted root mean squared deviation of the difference between predicted and measured values) of an ITC experiment in which cGAMP was titrated into a solution of Vs.4. The global best fit of three titrations indicated a dissociation constant (Kd) of 31.4 nM with a 68% confidence interval of 18–47.5 nM. c, X-ray crystal structure of hexameric Vs.4 (cartoon representation, one colour per monomer) bound to three molecules of cGAMP (green stick representation indicated by orange arrows). d, Composite omit map calculated with the cGAMP ligand omitted. Simulated annealing was used to remove any memory of the ligand. The difference density map (green) is contoured at 3.5σ with cGAMP (yellow) superimposed in the binding pocket that is formed between two monomers (cyan and orange). e, Detailed view of the residues forming π–π interactions with cGAMP. f, Detailed view of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges formed with cGAMP in the Vs.4 binding pocket. g, CapV was incubated with the indicated Vs.4 mutant (10 µM), cGAMP (1 µM) and resorufin butyrate (a fluorogenic phospholipase substrate) to measure the enzymatic activity of CapV. Bar graph represents average values ±s.d. of n = 3 technical replicates with individual points overlaid and is representative of two independent experiments.
