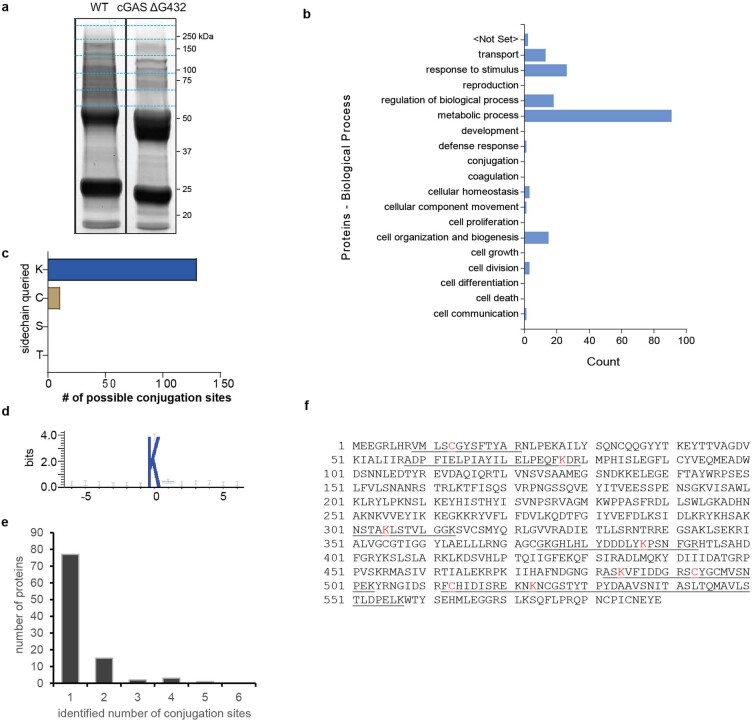
Extended Data Fig. 3. Identification of cGAS conjugation sites.
a, Flag-tagged cGAS and cGAS ΔG432 proteins were immunopurified from E. coli cells harboring the CBASS operons encoding these proteins. Isolated proteins were separated on SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie blue. Indicated protein bands were cut, alkylated, digested with trypsin, and analyzed by shot-gun LS-MS/MS analysis. Data is representative of three independent experiments: two with uninfected cells and one with cells infected with phage T4. b, Biological processes associated with proteins found to be conjugated by cGAS. c, The numbers of conjugation sites identified for lysine, cysteine, serine, and threonine is shown. d, Sequence alignment of the 130 cGAS conjugation sites surrounding the target lysine. e, Histogram of the number of conjugation sites per cGAS conjugated target. f, The protein sequence of Cap2. The cGAS conjugation sites are indicated in red and the peptides in which conjugation sites were identified by mass spectrometry are underlined. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.