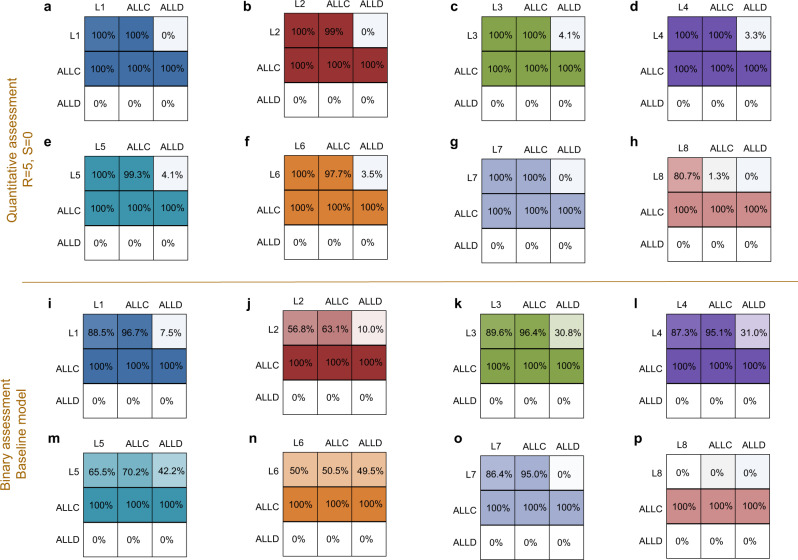
Fig. 3. Quantitative assessment improves the accuracy of reputation assignments by leading eight players.
We show the average overall judgments that players with the frame of reference R make of each other when comparing others’ reputation scores with the threshold (a–h). As the basis for comparison to the baseline model, we use the average images that players have of each other when they use the standard binary assessment (i–p). We observe that quantitative assessment and more nuanced reputations lead to a clear improvement of the accuracy with which players assign each other images. All leading eight norms achieve a perfectly correlated good self-image, as opposed to the baseline model, where only L1 (i) and L7 (o) achieve a self-image of more than 80% good. Players using quantitative assessment also do much better in judging ALLD as bad, and with the exception of the (less stable) L8 (h, p), also manage to assess ALLC as close to 100% good. This hints at the power of a more refined reputation dynamics. The parameters are the same as in Fig. 2.