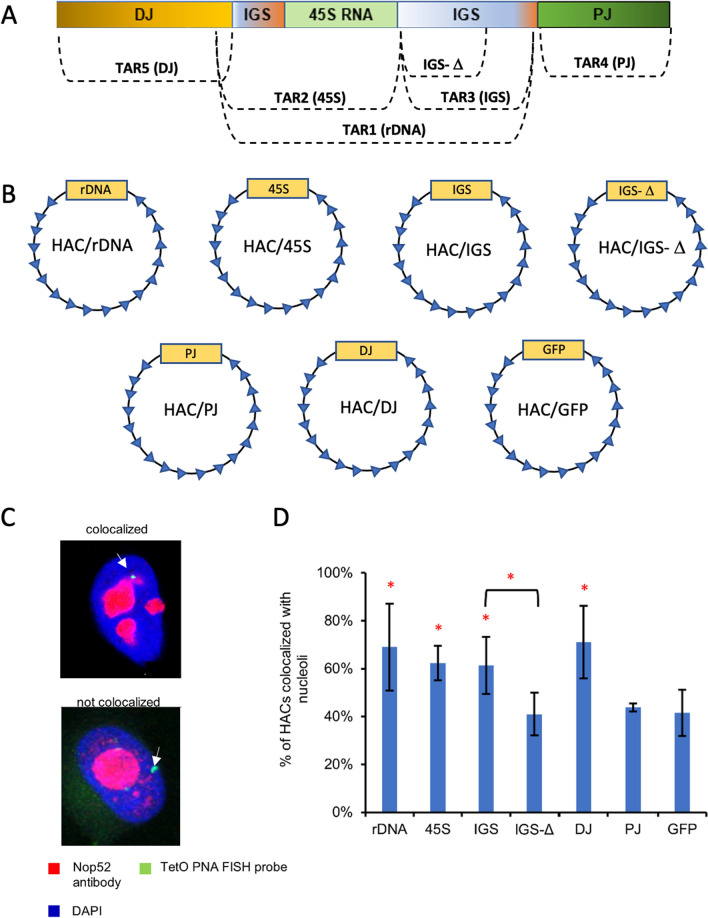
Fig. 3.
a TAR isolation of the rDNA repeat (rDNA; TAR1 construct), transcribed (45S; TAR2 construct) and non-transcribed (IGS; TAR3 construct) parts of the rDNA repeat, proximal junction (PJ; TAR4 construct) and distal junction (PJ; TAR5 construct) regions, and the IGS-Δ construct in which the 3′ end of the IGS sequence is deleted (see “Materials and methods” for detail). b Schemes of the HAC vector carrying either the rDNA repeat (HAC/rDNA), transcribed (HAC/45S) and non-transcribed (HAC/IGS) parts of the rDNA repeat, the PJ fragment (HAC/PJ), the DJ fragment (HAC/DJ) or the IGS-Δ BAC construct (HAC/IGS-Δ). A HAC carrying the GFP transgene (HAC/GFP) was used as a control. c 3D immuno-FISH in human HT1080 cells. Anti-RRP1 antibodies (Nop52) (red) used to visualize nucleoli were combined with the PNA probe for the alphoidtetO array of the HAC (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Nucleolar- and non-nucleolar-associated NORs are indicated by white arrowheads. d Quantification of 3D immuno-FISH showing the percentage of cells in which the HACs carrying different constructs are associated with mouse nucleoli. For each construct, the experiment was replicated three times (Table S5). Significant differences were calculated using a two-tailed nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. Statistically significant differences are marked with red asterisks