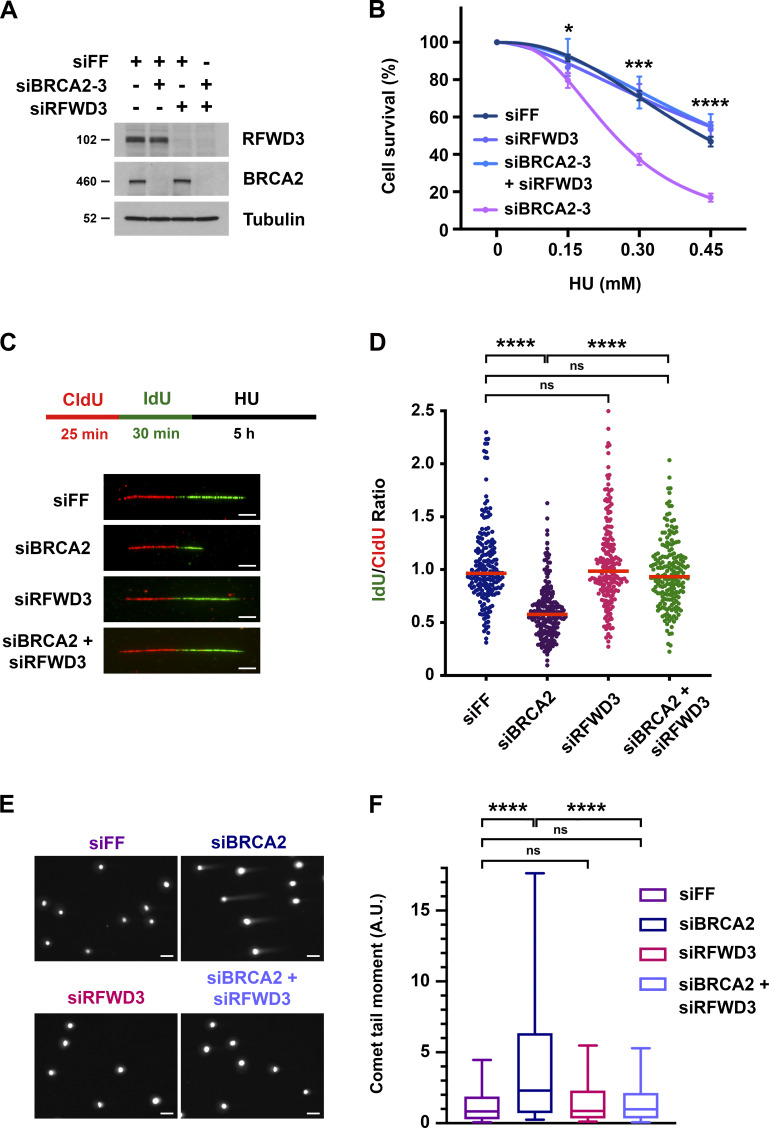
Figure 1.
Depletion of RFWD3 rescues HU sensitivity, nascent DNA degradation, and stalled fork collapse in BRCA2-deficient cells. (A) Detection of RFWD3 and BRCA2 levels in U2OS cells used in Fig. 1 B. (B) HU sensitivity of U2OS cells transfected with siBRCA2-3 and /or siRFWD3-4. Cell survival is normalized to the untreated control for each siRNA condition. Data represent the mean and SD of three replicates per HU dose and siRNA condition. Asterisks indicate P-values for RFWD3/BRCA2 versus BRCA2 depletion using an unpaired t test (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). Data are representative of three independent experiments, for which mean LC50 values are provided in Fig. S1 B. (C) Schematic for single DNA fiber analysis to detect nascent DNA degradation at stalled forks. U2OS cells transfected with siBRCA2-3 and /or siRFWD3-4 were labeled with sequential CldU (25 min) and IdU (30 min) and then treated with 2 mM HU (5 h). Representative images are provided for replication tracks containing both CldU and IdU from cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Scale bars, 5 µm. (D) IdU/CldU replication track ratios in U2OS cells treated as in Fig. 1 C. Median values from >200 replication tracks are represented by red lines (n.s., not significant; ****P < 0.0001; Mann Whitney test). (E) Representative images of neutral comet tails in U2OS cells transfected with siBRCA2-3 and/or siRFWD3-4 and treated with HU for 24 h. Scale bars, 50 µm. (F) Box plot of neutral comet-tail moments in U2OS cells from Fig. 1 E. Whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles. More than 300 cells were scored for each condition (n.s., not significant; ****P < 0.0001; Mann Whitney test).