Abstract
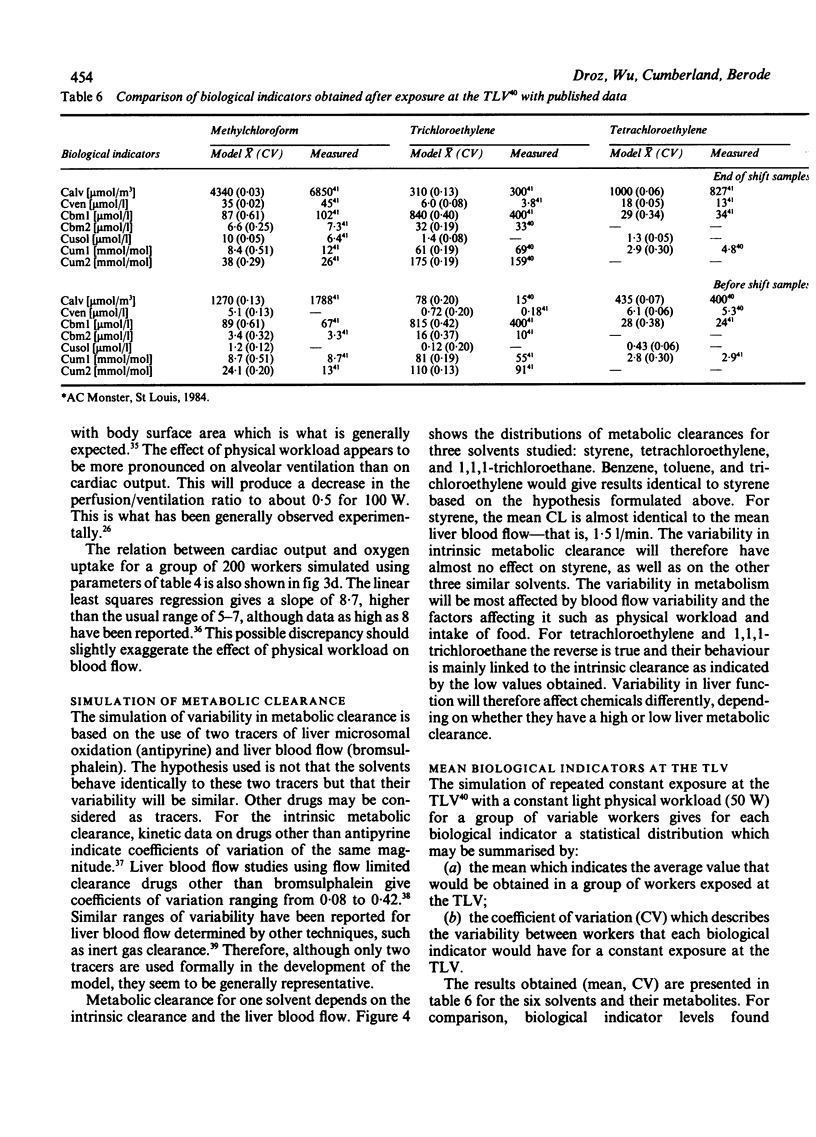
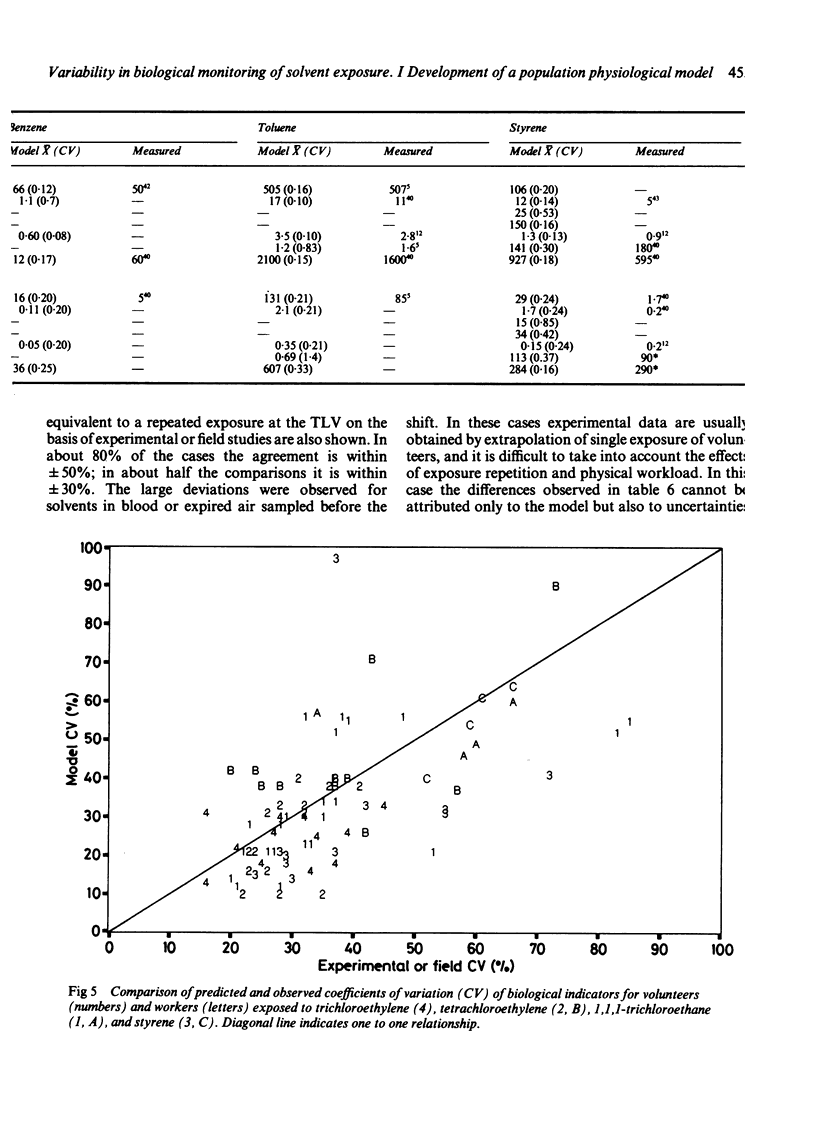
Biological indicators of exposure to solvents are often characterised by a high variability that may be due either to fluctuations in exposure or individual differences in the workers. To describe and understand this variability better a physiological model for differing workers under variable industrial environments has been developed. Standard statistical distributions are used to simulate variability in exposure concentration, physical workload, body build, liver function, and renal clearance. For groups of workers exposed daily, the model calculates air monitoring indicators and biological monitoring results (expired air, blood, and urine). The results obtained are discussed and compared with measured data, both physiological (body build, cardiac output, alveolar ventilation) and toxicokinetic for six solvents: 1,1,1-trichloroethane, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, benzene, toluene, styrene, and their main metabolites. Possible applications of this population physiological model are presented.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvan G. Individual differences in the disposition of drugs metabolised in the body. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Mar-Apr;3(2):155–175. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803020-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen M. E., Clewell H. J., 3rd, Gargas M. L., Smith F. A., Reitz R. H. Physiologically based pharmacokinetics and the risk assessment process for methylene chloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;87(2):185–205. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY S. E., INGELFINGER F. J., BRADLEY G. P. Hepatic circulation in cirrhosis of the liver. Circulation. 1952 Mar;5(3):419–429. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.5.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. H., Brooks C. S., Burch R. N. Clinical appraisal of creatinine clearance as a measurement of glomerular filtration rate. Am J Kidney Dis. 1982 Nov;2(3):337–346. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(82)80091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowles A. L., Borgstedt H. H., Gillies A. J. Tissue weights and rates of blood flow in man for the prediction of anesthetic uptake and distribution. Anesthesiology. 1971 Nov;35(5):523–526. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197111000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droz P. O., Fernandez J. G. Effect of physical workload on retention and metabolism of inhaled organic solvents. A comparative theoretical approach and its applications with regards to exposure monitoring. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1977 Feb 25;38(4):231–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00378335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droz P. O., Guillemin M. P. Human styrene exposure. V. Development of a model for biological monitoring. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;53(1):19–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00406174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond L., Luck R., Afacan A. S., Wilson H. K. Biological monitoring of workers exposed to benzene in the coke oven industry. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Apr;45(4):256–261. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.4.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIDANZA F., KEYS A., ANDERSON J. T. Density of body fat in man and other mammals. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Oct;6(4):252–256. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.6.4.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández J. G., Droz P. O., Humbert B. E., Caperos J. R. Trichloroethylene exposure. Simulation of uptake, excretion, and metabolism using a mathematical model. Br J Ind Med. 1977 Feb;34(1):43–55. doi: 10.1136/oem.34.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiserova-Bergerova V., Vlach J., Cassady J. C. Predictable "individual differences" in uptake and excretion of gases and lipid soluble vapours simulation study. Br J Ind Med. 1980 Feb;37(1):42–49. doi: 10.1136/oem.37.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. F. Drug kinetics and hepatic blood flow. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Nov-Dec;4(6):433–448. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guberan E., Fernandez J. Control of industrial exposure to tetrachloroethylene by measuring alveolar concentrations: theoretical approach using a mathematical model. Br J Ind Med. 1974 Apr;31(2):159–167. doi: 10.1136/oem.31.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin M. P., Bauer D. Biological monitoring of exposure to styrene by analysis of combined urinary mandelic and phenylglyoxylic acids. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1978 Nov;39(11):873–879. doi: 10.1080/0002889778507877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin M. P., Bauer D., Martin B., Marazzi A. Human exposure to styrene. IV. Industrial hygiene investigations and biological monitoring in the polyester industry. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1982;51(2):139–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00378158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbriani M., Ghittori S., Pezzagno G., Huang J., Capodaglio E. 1,1,1-Trichloroethane (methyl chloroform) in urine as biological index of exposure. Am J Ind Med. 1988;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T. Hepatic blood flow measurement with inert gas clearance. J Surg Res. 1986 Jul;41(1):92–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(86)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monster A. C. Difference in uptake, elimination, and metabolism in exposure to trichloroethylene, 1,1,1-trichloroethane and tetrachloroethylene. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1979 Jan 15;42(3-4):311–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00377785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monster A., Regouin-Peeters W., van Schijndel A., van der Tuin J. Biological monitoring of occupational exposure to tetrachloroethene. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1983 Jun;9(3):273–281. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. S., Rowland M. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a "well-stirred" model and a "parallel tube" model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Dec;5(6):625–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01059688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penno M. B., Dvorchik B. H., Vesell E. S. Genetic variation in rates of antipyrine metabolite formation: a study in uninduced twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5193–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey J. C., Andersen M. E. A physiologically based description of the inhalation pharmacokinetics of styrene in rats and humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 30;73(1):159–175. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowell L. B. Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jan;54(1):75–159. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. E., Watson I. D., Batt R. D. Total body water volumes for adult males and females estimated from simple anthropometric measurements. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Jan;33(1):27–39. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woiwode W., Drysch K. Experimental exposure to toluene: further consideration of cresol formation in man. Br J Ind Med. 1981 May;38(2):194–197. doi: 10.1136/oem.38.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womersley J. A comparison of the skinfold method with extent of 'overweight' and various weight-height relationships in the assessment of obesity. Br J Nutr. 1977 Sep;38(2):271–284. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womersley J., Durnin J. V., Boddy K., Mahaffy M. Influence of muscular development, obesity, and age on the fat-free mass of adults. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Aug;41(2):223–229. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi I., Komatsu E., Miyazawa K. Intersubject variability in cardiac output-O2 uptake relation of men during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2168–2174. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


