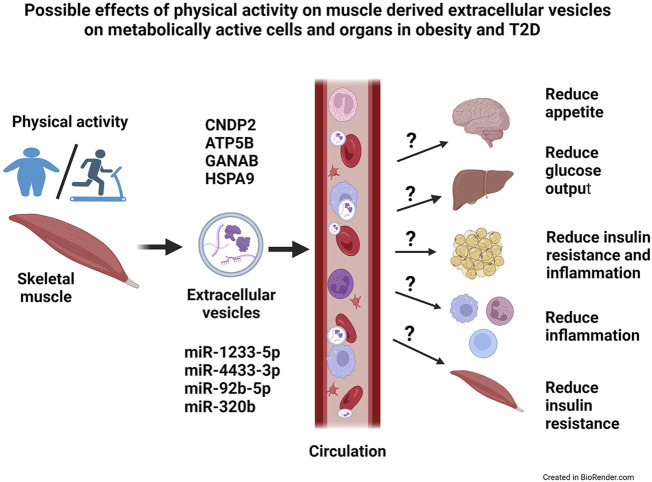
FIGURE 7.
Possible effects of physical activity on skeletal muscle-derived extracellular vesicles on metabolically active cells and organs in obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Skeletal muscles release extracellular vesicles (EVs) in response to exercise, and most likely will these EVs circulate and reach target organs. The EVs contain bioactive molecules, both microRNAs (miRs) and proteins, that might have a regulatory role on the metabolically active target cells and organs. Possibly, will EVs contribute to the health effects of exercise by reducing appetite, improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the low-grade inflammation in obesity and T2D. CNDP2 = cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase, ATP5B = ATP synthase subunit beta mitochondrial, GANAB = alpha-glucosidase AB, HSPA9 = stress-70 protein mitochondrial.