Figure 2.
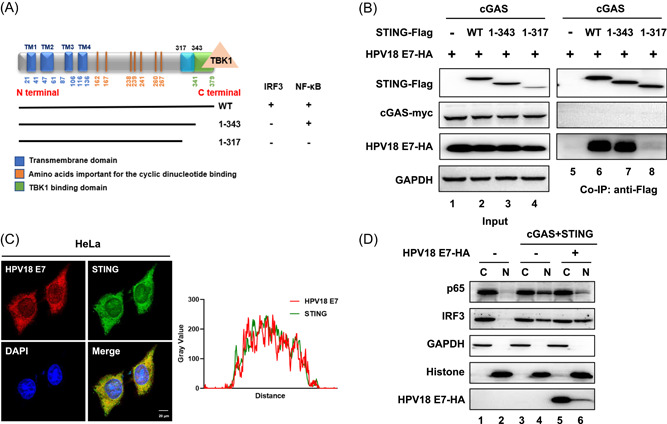
HPV18 E7 binds STING in a unique region and blocks the nuclear accumulation of p65 to inhibit NF‐κB signaling. (A) Schematic of the STING truncation constructs and functions of IRF3/NF‐κB activation. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc‐cGAS, HPV18 E7 and wild type or truncated STING‐Flag, as indicated. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis was performed as described above. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous HPV18 E7 and STING in HeLa cells was carried out and followed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The results were analyzed with ImageJ software to identify colocation of STING and HPV18 E7. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc‐cGAS and STING‐Flag in the presence or absence of HPV18 E7. The nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were separated and analyzed using immunoblotting. The results are shown for N = 3 independent experiments. NF‐κB, nuclear factor kappa‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cells; STING, stimulator of interferon gene.
