Figure 4.
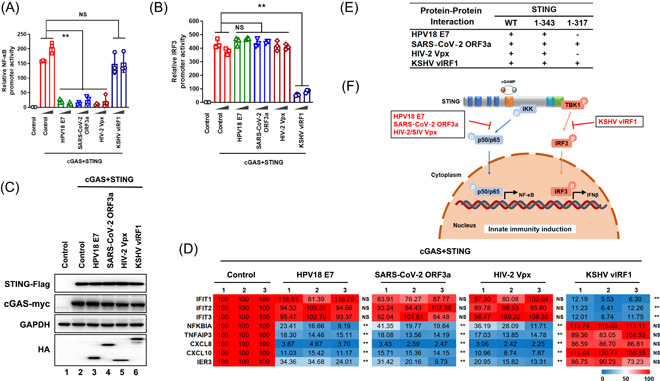
HPV18 E7, SARS‐CoV‐2 ORF3a, HIV‐2 Vpx, and KSHV vIRF1 selectively antagonize cGAS STING‐triggered innate immune activation. (A–C) HEK293T cells were transfected with NF‐κB‐Luc/IRF3‐Luc, pRL‐TK Renilla, Myc‐cGAS, and STING‐Flag in the presence or absence of vectors expressing different viral proteins, as indicated. Promoter activities (A and B) and protein expressions (C) were analyzed using luciferase reporter assays and immunoblotting, respectively. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc‐cGAS and STING‐Flag in the presence or absence of vectors expressing different viral proteins, as indicated. Total mRNA was extracted and analyzed by RT‐qPCR to determine the transcription levels of the indicated genes. (E) The protein‐protein interactions between different viral proteins and STING wild type or truncated. (F) Schematic representation of cGAS‐STING‐mediated NF‐κB and IRF3 signaling selectively antagonized by different viral proteins. Statistical significance was determined using a two‐sided unpaired t‐test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not significant). The results are shown for N = 3 independent experiments. HIV‐2, human immunodeficiency virus; mRNA, messenger RNA; NF‐κB, nuclear factor kappa‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cells; ORF3a, open reading frame 3a; RT‐qPCR, reverse‐transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; STING, stimulator of interferon gene; VPx, Viral protein X.
