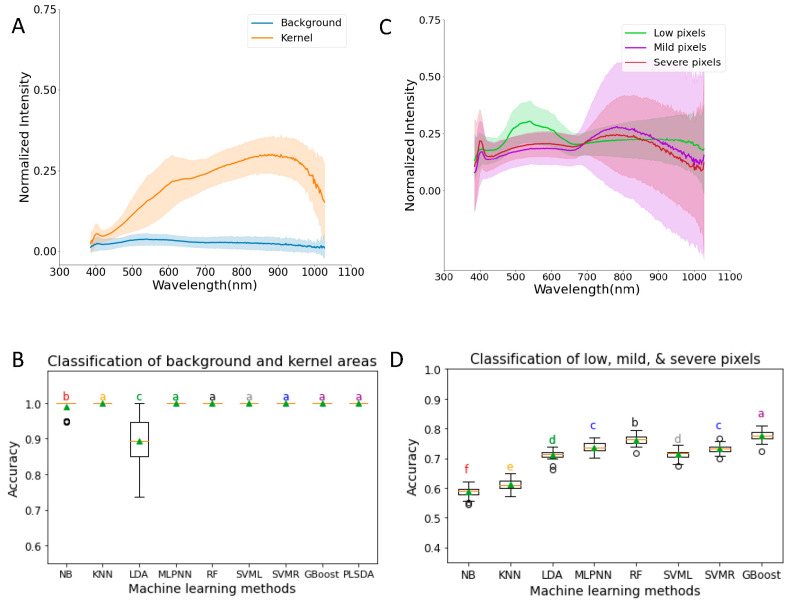
Figure 2.
(A) Spectral profile of background and kernel areas. (B) Comparison of the performance of nine machine learning methods to classify data points into background and kernel areas. (C) Spectral profiles of low, mild, and severe pixels. (D) Comparison of the performance of eight machine learning methods to classify pixel data points into low, mild, and severe classes. NB = Gaussian Naïve Bayes; KNN = K-nearest neighbors; LDA = linear discriminant analysis; MLPNN = multi-layer perceptron neural network; RF = random forests; SVML = support vector machine with linear kernel; SVMR = support vector machine with radial basis function kernel; G-Boost = gradient boosting; PLSDA = Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis. All data in (A,C) are normalized with a maximum value of 1.0. Letters a–f in (B,D) indicate statistical test results with same letter representing that the difference is not statistically significant.